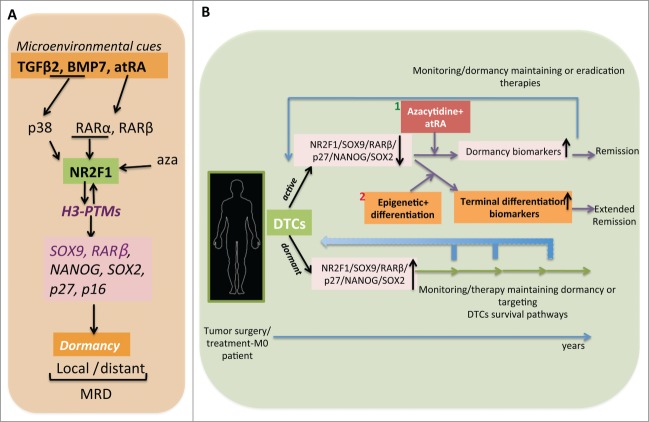
Figure 1.
Dormancy programs and their potential use in patient treatment. (A) Microenvironmental cues such as retinoids and stress signals enforce epigenetic changes in NR2F1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group F, member 1) expression and activate an NR2F1-dependent dormancy program in local and distant residual tumor cells. This signature is defined by the re-expression of genes in the retinoic acid, pluripotency, and cell cycle inhibitor pathways. Moreover, NR2F1 maintains active histone markers on SOX9 (SRY [sex determining region Y]- box 9) and RARβ (retinoic acid receptor, β) promoters in dormant cells. However, at the same time NR2F1 is also responsible for a globally repressive chromatin state. Lastly, all trans retinoic acid (atRA) in combination with azacytidine (aza) enforces a long-sustained NR2F1-induced dormancy program. H3-PTMs, histone 3-post-translational modifications; MRD, minimal residual disease. (B) Possible therapeutic scenarios for patients with long-term MRD. Disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) collected from bone marrow (BM) of M0 stage patients (distant metastases are not detected) could be analyzed to determine their dormant or active status and select the appropriate therapeutic action. For example, if DTCs carry a dormancy signature (NR2F1high/NR2F1 targetshigh) either dormancy maintaining therapy could be applied or therapies that eliminate these cells could be used (lower part of the panel); if DTCs carry a signature indicative of reactivation (NR2F1low/NR2F1 targetslow) then the azacytidine+atRA therapy that we propose here may serve to convert these residual tumor cells back to dormancy. This combination might also benefit from the addition of inhibitors of the mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK1) pathway (1). DTCs from BM aspirates could be tested for restoration of dormancy biomarkers and to examine the long-lasting treatment efficacy over years. Patients under this scenario would be considered in remission. Alternatively, the design of treatments that allow terminal differentiation of residual tumor cells would entirely prevent the reawakening of DTCs and induce an extended long-term remission phase (2).