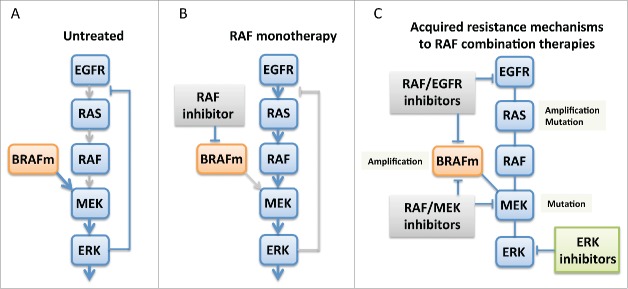
Figure 1.
RAF inhibitors for the treatment of colorectal carcinomas bearing BRAF mutations. (A) Constitutively active BRAF strongly activates MAPK signaling, leading to ERK activation. Downstream of ERK, inhibitory signals reduce upstream inputs into MAPK. (B) With RAF inhibitor monotherapy, activity of mutant BRAF is reduced. This decreases the inhibitory feedback that typically occurs downstream of ERK and allows activation of RAS and wild-type RAF, leading to reactivation of MAPK signaling. (C) Mechanisms of clinical acquired resistance emerge in patients with BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer treated with RAF/EGFR or RAF/MEK inhibitor combinations. Despite these resistance mechanisms, ERK inhibition can suppress MAPK signaling and overcome resistance in laboratory models.