Figure 4.
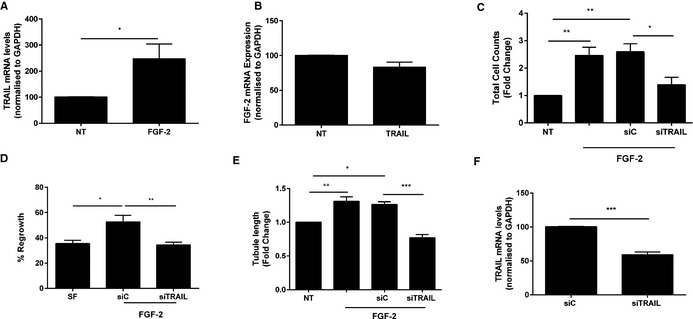
The proangiogenic effects of FGF‐2 are TRAIL dependent. A, FGF‐2 increases TRAIL mRNA expression in ECs. HMEC‐1 cells were serum starved followed by FGF‐2 (50 ng/mL) treatment for 24 hours prior to RNA extraction and real‐time PCR. B, FGF‐2 mRNA expression in ECs was unchanged. HMEC‐1 cells were serum starved followed by TRAIL (10 ng/mL) treatment for 24 hours prior to RNA extraction and real‐time PCR. TRAIL siRNA inhibits (C) FGF‐2‐inducible proliferation and (D) migration of ECs. Serum‐arrested HMEC‐1 cells were transfected with 200 nmol/L TRAIL siRNA or AllStar control siRNA (siC) for 3 to 6 hours prior to FGF‐2 treatment. Total cell counts were assessed 72 hours later and migration assessed 24 hours later. E, TRAIL siRNA blocks tubule formation inducible by FGF‐2. Growth quiescent HMEC‐1 cells were transfected with siC or siTRAIL (200 nmol/L) overnight. Cells were then seeded into growth factor reduced Matrigel in serum‐free media. Cells were treated with FGF‐2. Tubule formation was photographed and tubule length quantified. F, TRAIL siRNA inhibits TRAIL mRNA expression; mRNA was normalized to GAPDH. Data represent the combined results of at least 3 independent experiments. Results are expressed as mean±SEM; t test or 1‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni comparison; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. ECs indicates endothelial cells; FGF‐2, fibroblast growth factor‐2; HMEC‐1, human microvascular endothelial cell‐1; NT, no treatment; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; TRAIL, tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis‐inducing ligand.
