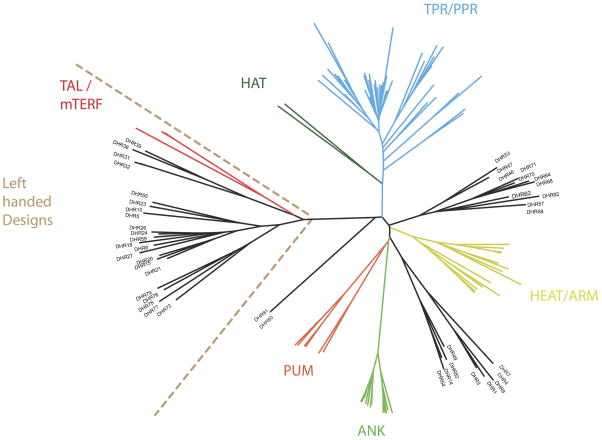
Extended Data Figure 8. Structural similarity between DHRs and repeat protein families.
DHRs cluster separately from existing repeat proteins. DHRs are equally distributed between right-handed and left-handed repeats, as referred to the repeat handedness, in contrast to known alpha helical repeat proteins, which are mostly right-handed. This result indicates that the handedness observed in known families is not an intrinsic limitation of repeat proteins structures. Repeat handedness, as defined by Kobe and Kajava6, indicates the rotation of the main chain going from the N- to the C-terminal around the axis connecting the repeat centers of mass. The structural similarity tree was built using pairwise comparison as measured by TM-score.