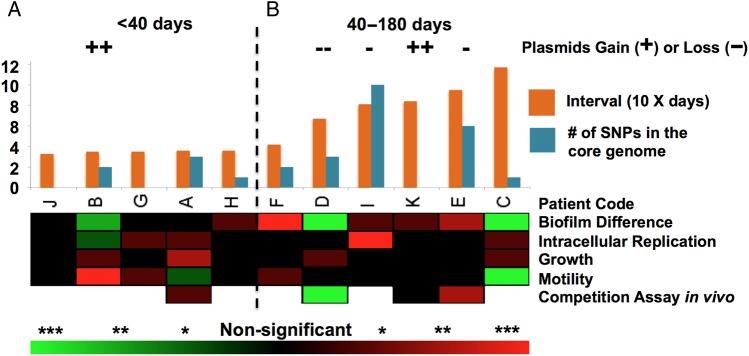
Figure 1.
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium genetic and phenotypic dynamics during persistent infection. A, Accumulation of genetic mutation, including number of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the core genome, and variations, such as large genomic elements gain or loss, are correlated with interval time of the isolates. In general, patient samplings interval within 40 days have less genetic changes than samples of interval days over 40. B, The summary results for the phenotypic assays between early and later persistent isolates for each patient. The heatmap shows phenotypic changes between the early and later isolates, red indicates later isolate show an increasing phenotypic fitness when comparing with early isolate, whereas green suggests a decreasing phenotypic fitness when comparing with early isolate. The color density represents if the change between early and later persistent strain is statistically different. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001.