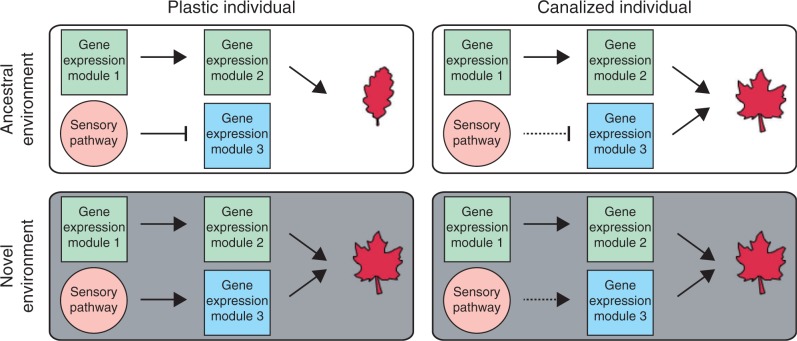
Fig. 4.
Examining how changes in gene regulatory networks contribute to genetic assimilation. Expression analysis across development can be employed to determine transcriptional changes that enable constitutive expression of a phenotype. Comparison of plastic and canalized genotypes in the ancestral and novel environment can be used to identify gene modules that underlie canalization. Here, we have shown a hypothetical example of what might be found in such a study. In the example, the sensitivity of gene expression module 3 to regulation by an environmentally responsive sensory pathway has been reduced in canalized individuals (indicated by a dotted line). Due to this reduction, gene expression module 3 is expressed when individuals are not reared in the novel, inductive environment. This higher expression leads to constitutive expression of the new trait across conditions.