FIGURE 2.
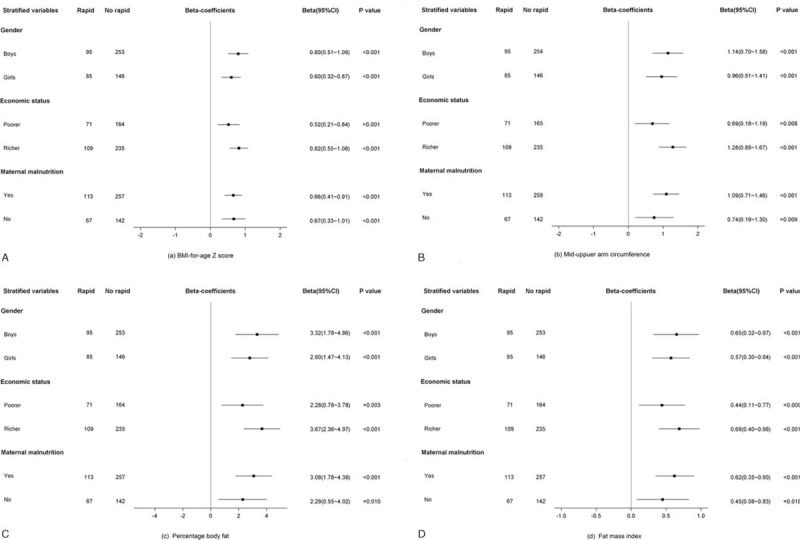
(A) The effect of rapid infancy weight gain on BMI-for-age Z score at early school age by gender, economic status at early school age, and maternal nutritional status at enrollment. (B) The effect of rapid infancy weight gain on mid-upper arm circumference at early school age by gender, economic status at early school age, and maternal nutritional status at enrollment. (C) The effect of rapid infancy weight gain on percentage body fat at early school age by gender, economic status at early school age, and maternal nutritional status at enrollment. (D) The effect of rapid infancy weight gain on fat mass index at early school age by gender, economic status at early school age, and maternal nutritional status at enrollment. 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; reference category: no rapid weight gain between birth and 1.5 years; three-level mixed analysis was used, with adjustments for gender, age, birth weight, gestational age, economic status at early school age, parental educational level, occupation, height, BMI, maternal malnutrition at enrollment, antenatal micronutrient supplementation, birth order, infant feeding method, activity level, and medical history. BAZ = body mass index-for-age Z scores, BMI = body mass index, CI = confidence interval, FMI = fat mass index, MUAC = mid-upper arm circumference, PBF = percentage body fat.
