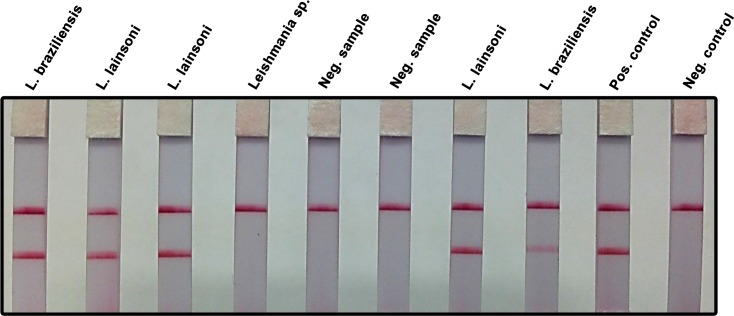
Fig 3. RPA-LF amplification of clinical samples using a simplified DNA extraction method.
Samples from patients suspected of having cutaneous leishmaniasis were obtained by pressing Whatman FTA filter paper (two 6 mm diameter discs) over the dermal lesions. Two, 3 mm diameter papers were cut from the original samples using a punch, washed thrice with FTA washing reagent and twice with TE buffer pH 8. A 2.5 μL aliquot was amplified by RPA and subsequently read using a lateral flow strip. Patients infected with Leishmania Viannia spp. (L. lainsoni, L. braziliensis) were readily detected. The test did not amplify a strain originally labeled as Leishmania sp. in NAMRU-6, Peru. Presumably, it did not belong to the Viannia subgenus as confirmed by real-time PCR at UTMB. There was agreement between NAMRU-6 and UTMB labs with regard to the negative clinical samples. L. lainsoni was used as positive control; the negative control was run without template.