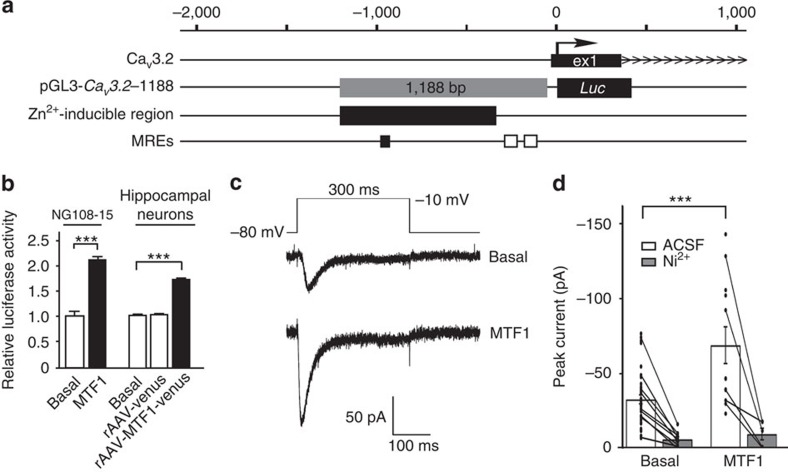
Figure 4. MTF1 mediates the activation of CaV3.2 promoter by Zn2+ and increases functional expression of CaV3.2.
(a) Schematic overview of the rat CaV3.2 promoter region with the CaV3.2-1188 promoter–luciferase reporter construct20. The identified Zn2+-inducible region is indicated (black box) together with the three MREs. One MRE is located within the Zn2+-inducible region (black bar), whereas two MREs are located outside the Zn2+-inducible region (white bars). (b) Left panel: luciferase activity of the CaV3.2 promoter construct after transfection with MTF1 in NG108-15 cells. Right panel: luciferase activity of the CaV3.2 promoter in rat hippocampal neurons transduced with rAAV particles harbouring the rat CaV3.2 promoter luciferase reporter (rAAV-CaV3.2) (ref. 39), a pRL-TK control promoter construct, an expression construct for MTF1 (rAAV-CMV-MTF1-IRES-Venus) or a control expression construct (rAAV-CMV-Venus) at DIV1 and measured at DIV15 (t-test: ***P≤0.001; n=3). (c) Ca2+ currents in NG108-15 cells were elicited with a voltage step from −80 to −10 mV (upper part). Representative current traces show an increased amplitude in MTF1-transfected cells (lower trace) compared with controls (upper trace). (d) Average of the transient Ca2+ currents for control cells (n=37) and cells transfected with MTF1 (n=12) display the functional upregulation of T-type Ca2+ currents (t-test: ***P≤0.001). Average of the transient currents after application of 100 μM Ni2+ showed the large amplitude reduction in all recorded cells (n=9 for basal conditions and n=5 following Zn2+ application), indicating involvement of CaV3.2 channels.