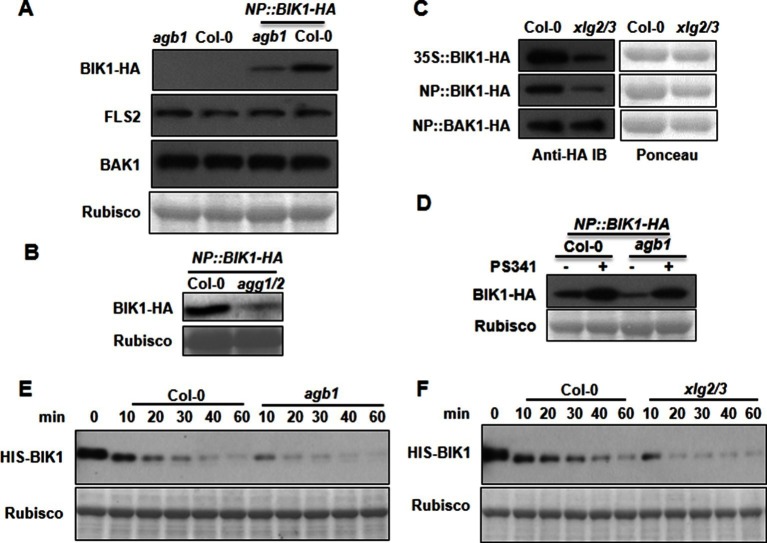
Figure 3. G proteins positively regulate immunity and BIK1 stability.
(A) AGB1 is required for accumulation of BIK1, but not FLS2 and BAK1. BIK1-HA was introduced into agb1 by crossing, homozygotes of the indicated genotypes in F3 generation were used for immunoblot analyses. (B) AGG1/2 are required for BIK1 stability. NP::BIK1-HA was introduced into agg1/2 by crossing, homozygous plants in F3 generation were subject to immunoblot analyses. (C) XLG2/3 are required for BIK1 accumulation. NP::BIK1-HA, 35S::BIK1-HA and NP::BAK1-HA plasmids were transiently expressed in WT and xlg2/3 protoplasts, and accumulation of BIK1 and BAK1 was determined by immunoblot analyses. (D) AGB1 regulates BIK1 accumulation through the proteasome pathway. One-week-old NP::BIK1-HA seedlings of WT (Col-0) or agb1 background were pretreated with DMSO (-) or 100 μM proteasome inhibitor PS341(+) for 8 hr before total protein was isolated for immunoblot analysis. (E) The agb1 extract shows accelerated degradation of BIK1 in vitro (F) The xlg2 xlg3 extract shows accelerated degradation of BIK1. Total extracts from WT (Col-0), agb1 and xlg2 xlg3 seedlings were incubated with HIS-BIK1 protein at 22°C for the indicated times, and equal amounts of sample were analyzed using anti-HIS immunoblot. Each experiment was repeated at least three times, and data from one representative experiment are shown.
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. G proteins are required for BIK1 stability.
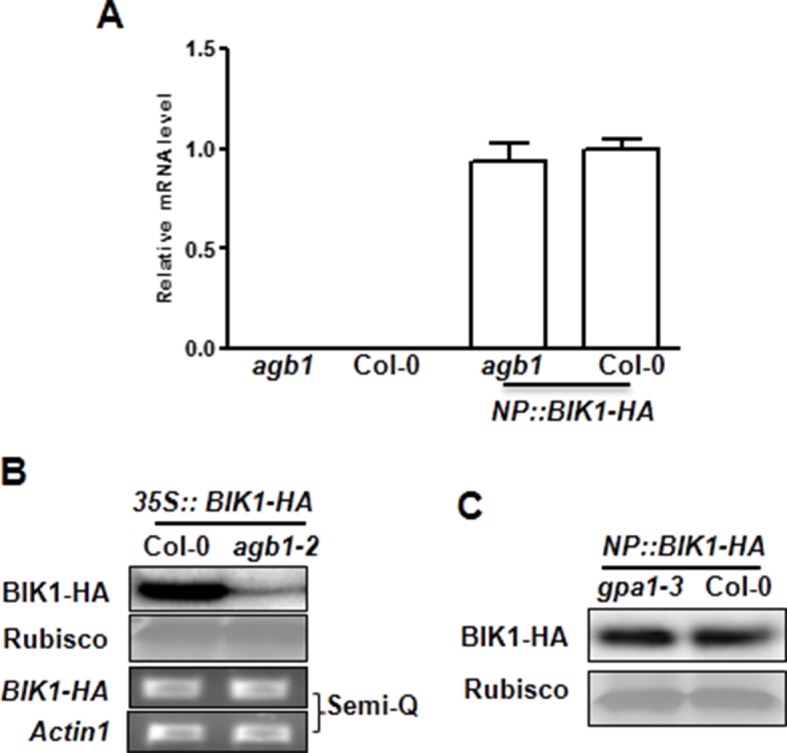
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. AGB1 regulates BIK1 stability through proteasome pathway.
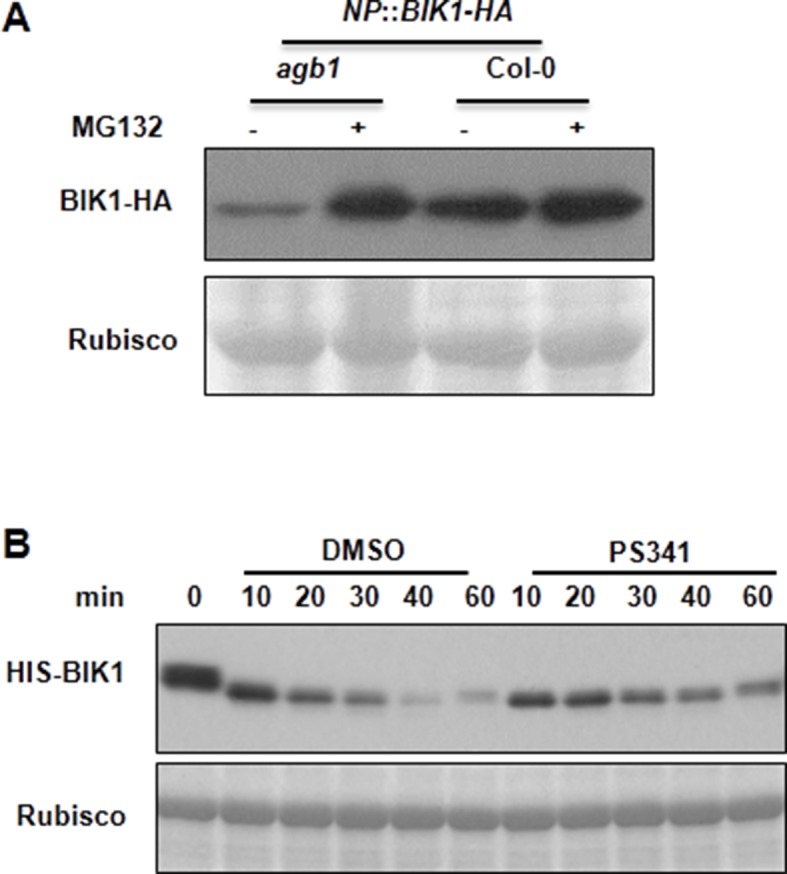
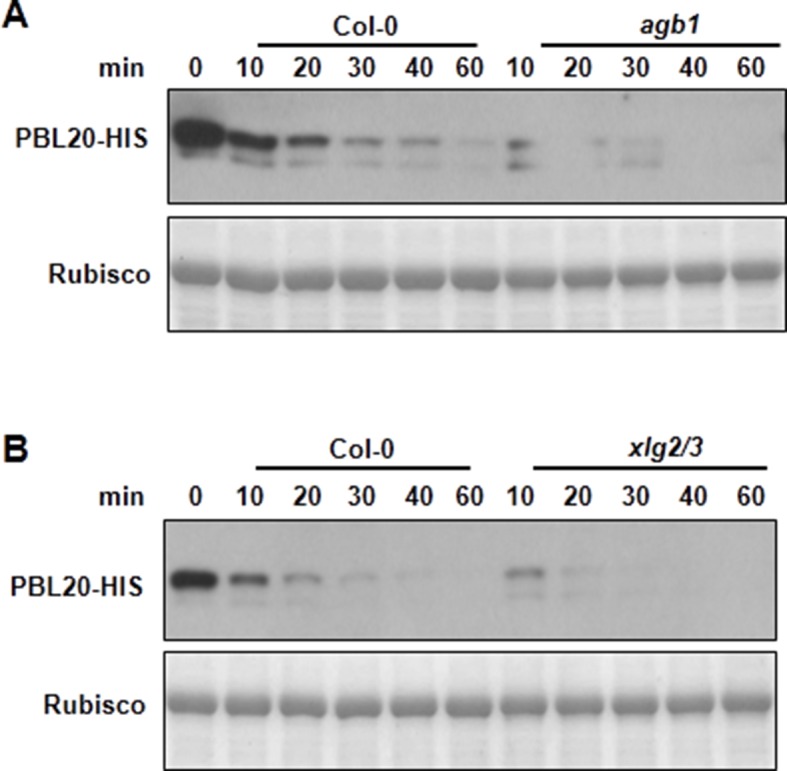
Figure 3—figure supplement 3. AGB1 and XLG2/3 attenuate PBL20 degradation.