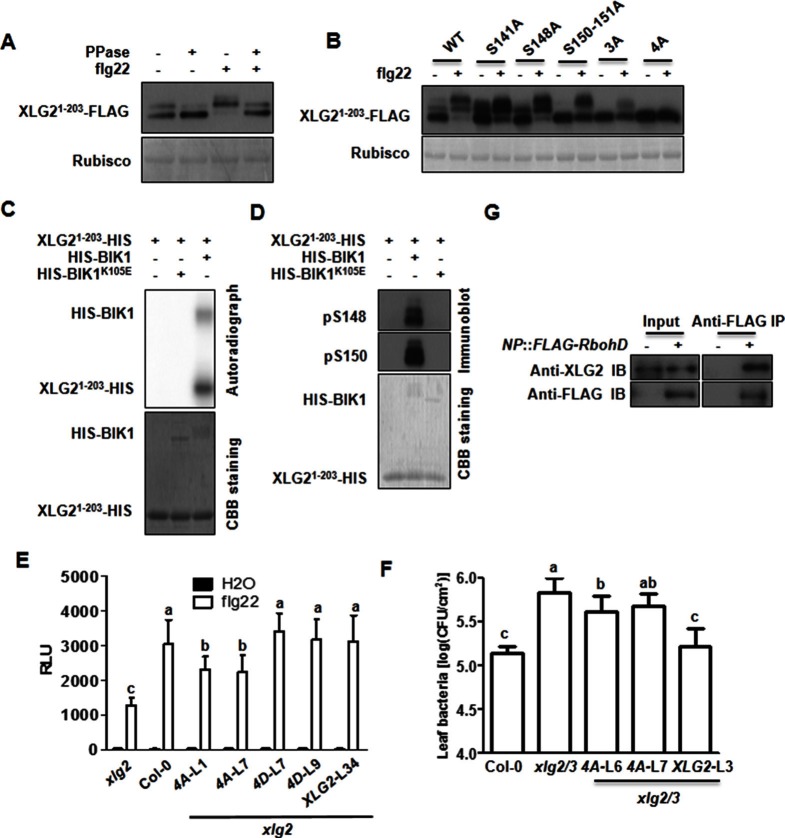
Figure 5. Phosphorylation of XLG2 by BIK1 regulates flg22-induced ROS.
(A) Flg22-induces phosphorylation of XLG2 in the N terminus. Protoplasts expressing XLG21-203-FLAG were treated with flg22. The total protein was treated with (+) or without (-) λ protein phosphatase (PPase) prior to anti-FLAG immunoblot analysis. (B) Flg22-induced phosphorylation of XLG2 in protoplasts primarily occurs in Ser141, Ser148, Ser150 and Ser151. Different mutated form of XLG21-203-FLAG constructs were transiently expressed in WT protoplast, treated with flg22 and the migration of XLG21-203-FLAG were examined by anti-FLAG immunoblot. (C) BIK1 phosphorylates XLG2 N terminus in vitro. XLG21-203-HIS was incubated with HIS-BIK1 and HIS-BIK1K105E in the presence of 32P-γ-ATP and analyzed by autoradiography. CBB, coomassie brilliant blue. (D) BIK1 phosphorylates XLG2 at Ser148 and Ser150 in vitro. XLG21-203-HIS was incubated with HIS-BIK1 and HIS-BIK1K105E in kinase reaction buffer. Protein phosphorylation was detected by anti-pSer148 and pSer150 immunoblots. (E) XLG2 phosphorylation is required for flg22-induced ROS. xlg2 mutant plants were transformed with WT (NP::XLG2-L34), non-phosphorylatable (4A-L1 and 4A-L7), or phospho-mimicking (4D-L7 and 4D-L9) forms of XLG2 under control of the native XLG2 promoter. Independent T2 lines were examined for flg22-induced ROS burst and peak relative luminescence unit (RLU) values are shown. (mean ± SD; n ≥ 6; p<0.05, Student’s t-test; different letters indicate significant difference). (F) XLG2 phosphorylation is required for Pst resistance. xlg2/3 double mutant plants were transformed with WT (XLG2-L3) or non-phosphorylatable (4A-L6 and 4A-L7) form of XLG2 under control of the native XLG2 promoter. Independent T2 lines were inoculated with Pst, and bacterial populations in leaves were measured 3 days post inoculation. (mean ± SD; n ≥ 6; p<0.05, Student’s t-test; different letters indicate significant difference). (G) XLG2 interacts with RbohD in Arabidopsis plants. rbohD plants were transformed with the FLAG-RbohD transgene under control of the RbohD native promoter. The resulting plants were used for Co-IP assay. Each experiment was repeated two (C, G) or three (A, B, D–F) times, and data of one representative experiment are shown.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.13568.018
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. The N terminus of XLG3, but not XLG1, is phophorylated upon flg22-treatment.
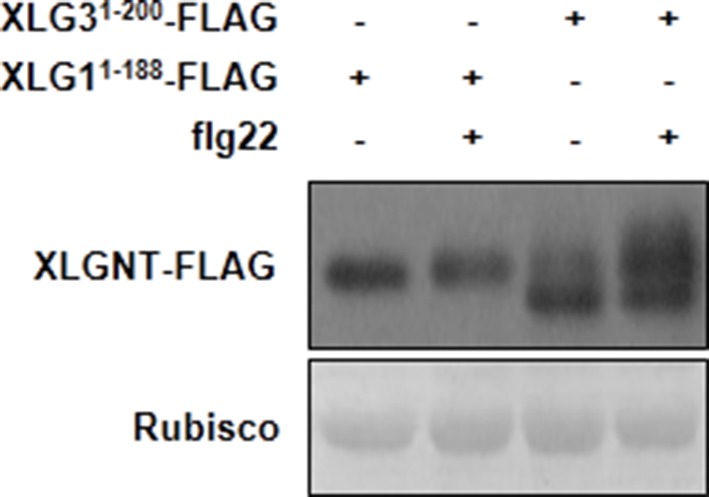
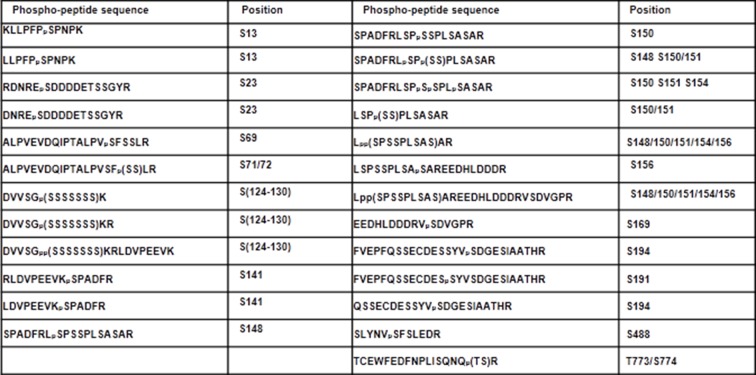
Figure 5—figure supplement 2. Phospho-sites in XLG2 isolated from flg22-treated protoplasts.
Figure 5—figure supplement 3. Mutations that block or mimic XLG2 phosphorylation do not impact BIK1 stability and XLG2-BIK1 interaction.
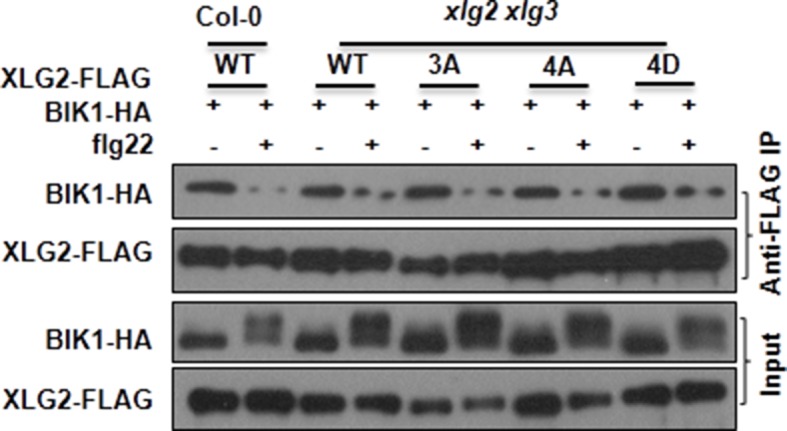
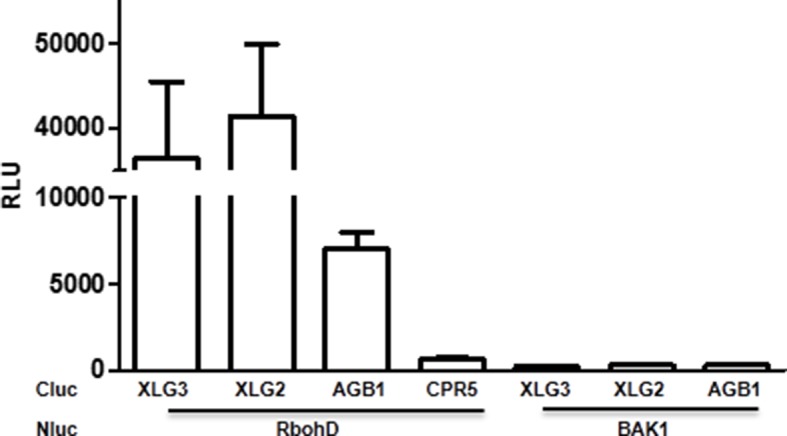
Figure 5—figure supplement 4. XLG2/3 interact with RbohD in Nb plants.