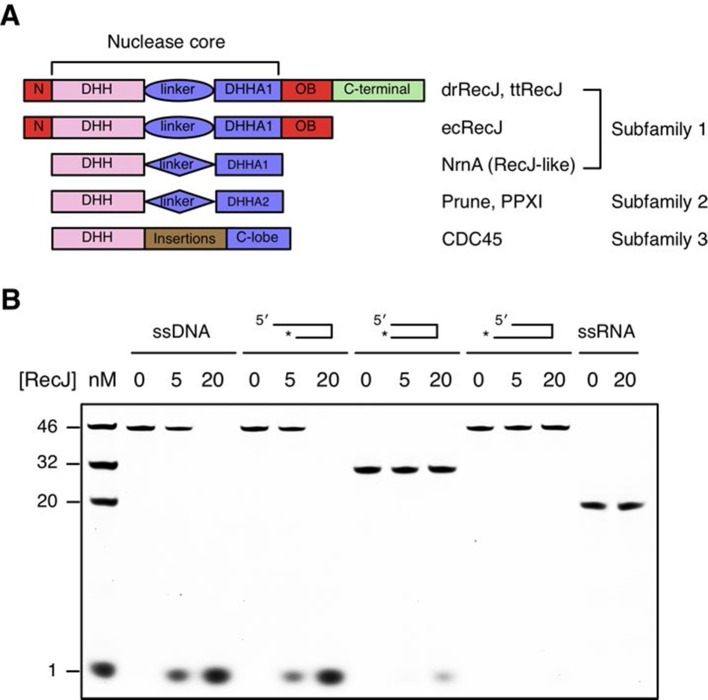
Figure 1. Domain arrangement and substrate specificity of drRecJ.
(A) Schematic of the domain arrangements of three DHH subfamilies. (B) Denaturing PAGE gel showing that drRecJ degrades different substrates, as shown at the top of the panel. 3′-Fluorescent labeled DNA or RNA (100 nM) were incubated with drRecJ (0, 5 and 20 nM) in the presence of 100 nM Mn2+ (see methods).
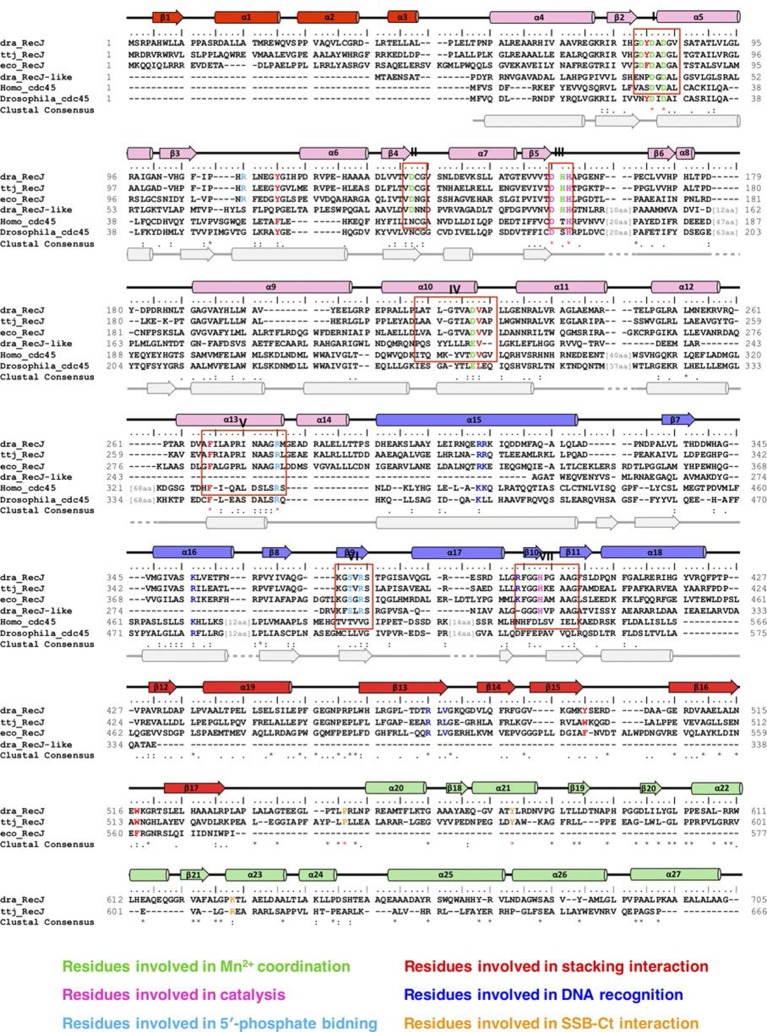
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Sequence alignments, secondary structure, and functional residues of RecJ and CDC45.
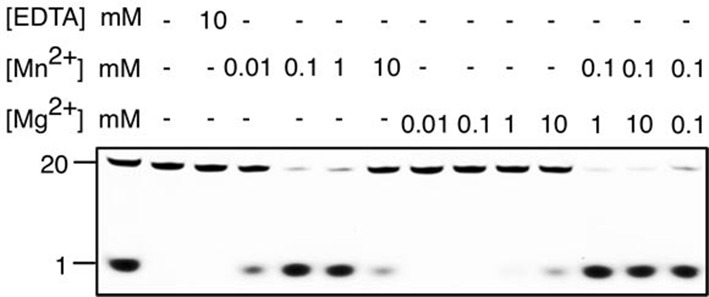
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Metal preference of drRecJ.