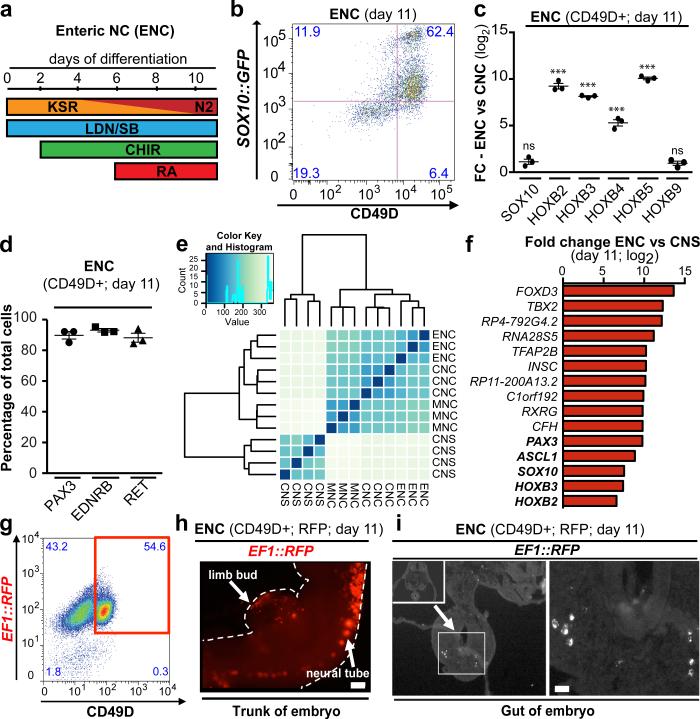
Figure 1. Deriving ENC precursors from hESCs.
a) Protocol (day 0-11) for deriving enteric NC (ENC) cells. b) Flow cytometry of ENC for SOX10::GFP and CD49D at day 11. c) qRT-PCR for SOX10, vagal NC markers HOXB2-5 and HOXB9 in CD49D+ ENC versus CNC, n=3 independent experiments. d) Quantification of PAX3, RET and EDNRB immunofluorescence in CD49D+ ENC, n=3 independent experiments. e) Unsupervised clustering of CD49D+ NC versus matched CNS precursor (day 11). f) Top 10 and selected additional (bold) differentially expressed transcripts in CD49D+ ENC versus CNS precursors. g) RFP+ and CD49D+ ENC are FACS purified (day 11) for transplantation into developing chick embryos. h) Whole mount epifluorescence showing distribution of RFP+ cells 24 hours after injection. i) Cross section of the embryos at trunk levels shows RFP+ cells located in the gut anlage (left panel) and at higher magnification (right panel). Scale bar = 200 μm in i; 10 μm in j; Data are mean ± SEM. p-values are: *** p < 0.001 (t-test, ENC compared to CNC; n=3)