Fig. 4. Deterministic control of quantum interferences.
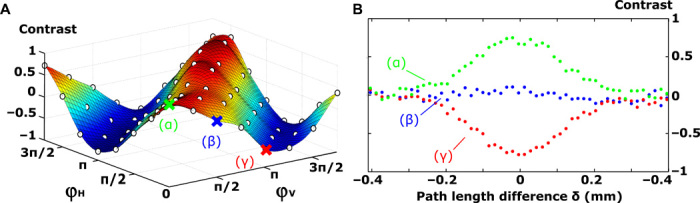
(A) Nonclassical interference contrast measured for two photons mapped onto a superposition of two output states with different phase settings (ϕH, ϕV). The nonclassical contrast is defined as C = (Rδ=0 − Rδ=0.4 mm)/Rδ=0.4 mm, where Rδ is the two-photon coincidence rate of the targeted output state at a path length difference of δ. Contrast values are measured with 8 × 8 = 64 phase settings. (B) Contrast values for three phase settings [(α), (ϕH = 0, ϕV = 0); (β), (ϕH = 0, ϕV = π/2); (γ), (ϕH = 0, ϕV = π)] as a function of the path length difference between input photons δ. The observed effects are consistent with the initial indistinguishability of the photons evaluated with a HOM experiment (see the Supplementary Materials). Data are acquired for 290 s with a coincidence window of 2.5 ns.
