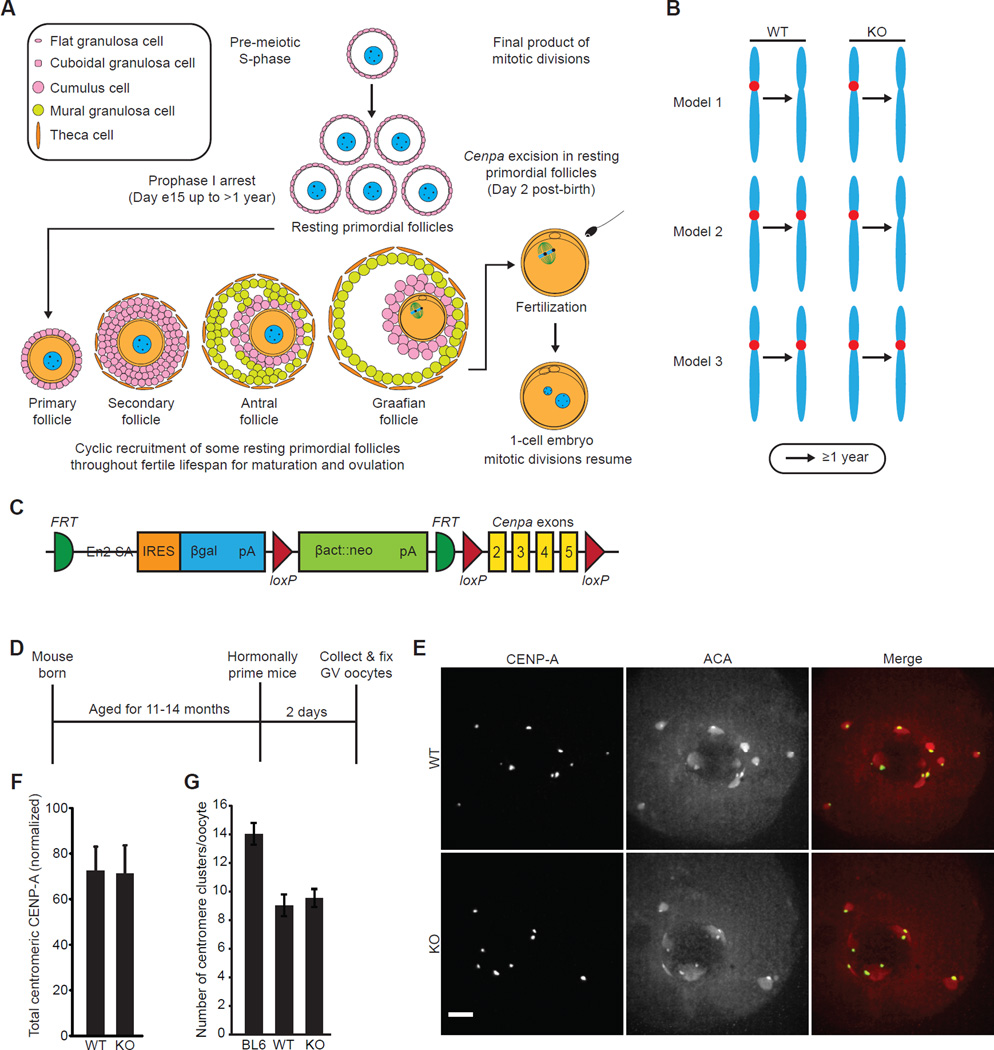
Figure 2. CENP-A nucleosomes are stably retained at oocyte centromeres for >1 year.
(A) Oocytes arrest in prophase I in resting primordial follicles, which are cyclically recruited starting five days after birth to begin growth towards a Graafian follicle, the final stage before ovulation. Primordial follicles can remain in the resting phase for a period lasting >1 year before they are recruited for maturation and ovulation. After fertilization, the maternal and paternal pronuclei enter G1-phase and begin mitotic cell cycles. Cre expression driven by the Gdf9 promoter excises Cenpa in resting primordial follicles two days after birth. (B) Three models for centromere inheritance in the mammalian oocyte. See Results & Discussion for details. (C) Schematic of Cenpa conditional knockout gene locus. The neomycin selection cassette used for selection of ES cells is flanked by FRT sites. Cenpa protein coding exons 2–5 are flanked by loxP sites. (D–F) Oocytes were collected from 11–14.5 month old WT and KO mice, or from young C57BL/6J (BL6) controls, and CENP-A levels were analyzed by immunofluorescence, with ACA to co-label centromeres (schematic, D). Images (E) of oocytes with intact germinal vesicles (GV) are maximal intensity projections of confocal z-series; scale bar 5 µm. Total centromeric CENP-A staining was quantified for each oocyte (n=64 oocytes from 4 WT mice; n=85 oocytes from 5 KO mice) and normalized to young C57BL/6J controls (n=155 oocytes, 8 mice) for each experiment. Normalized values were averaged over multiple experiments (F; error bars, s.d.). (G) The number of centromere clusters was counted in each oocyte and averaged over each group (error bars, s.d.). See also Figures S2, S3, S4, and Table S1.