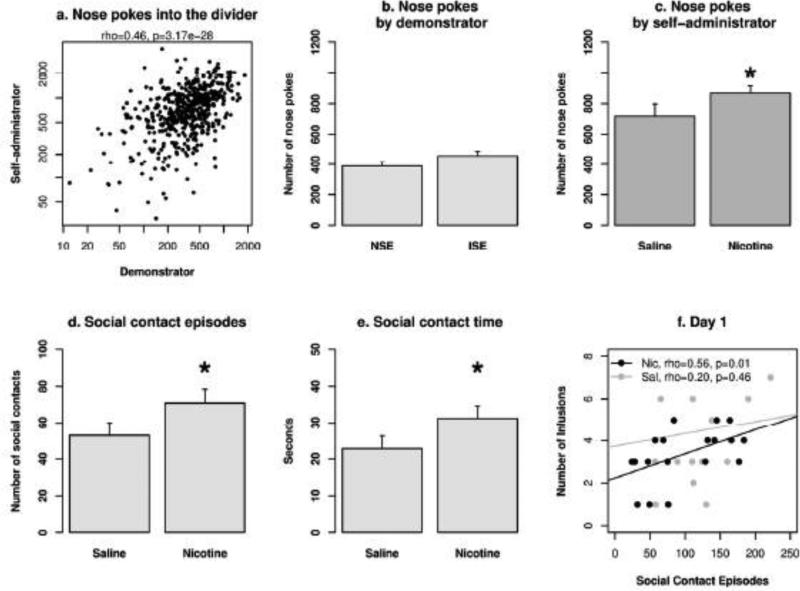
Fig. 4. Social interaction during nicotine IVSA sessions.
a) The highly significant correlation on the number of nose pokes per session between the two rats indicated the social nature of this behavior in our model. b) The social environment did not have a significant effect on the number of nose pokes produced by the demonstrator rats. c) Rats that self-administered i.v. nicotine produced a greater number of nose pokes compared to those that self-administered i.v. saline. d) and e) The effect of nicotine on social interaction was confirmed by analyzing the number of social contact episodes and the amount of time spend on social interaction via the holes in the divider. f) The number of social contact episodes for ISE groups was positively correlated with the number of infusions on the first day of IVSA for the nicotine but not the saline group. ISE: inducing social environment. NSE: neutral social environment. *: p < 0.05 compared to the saline group.