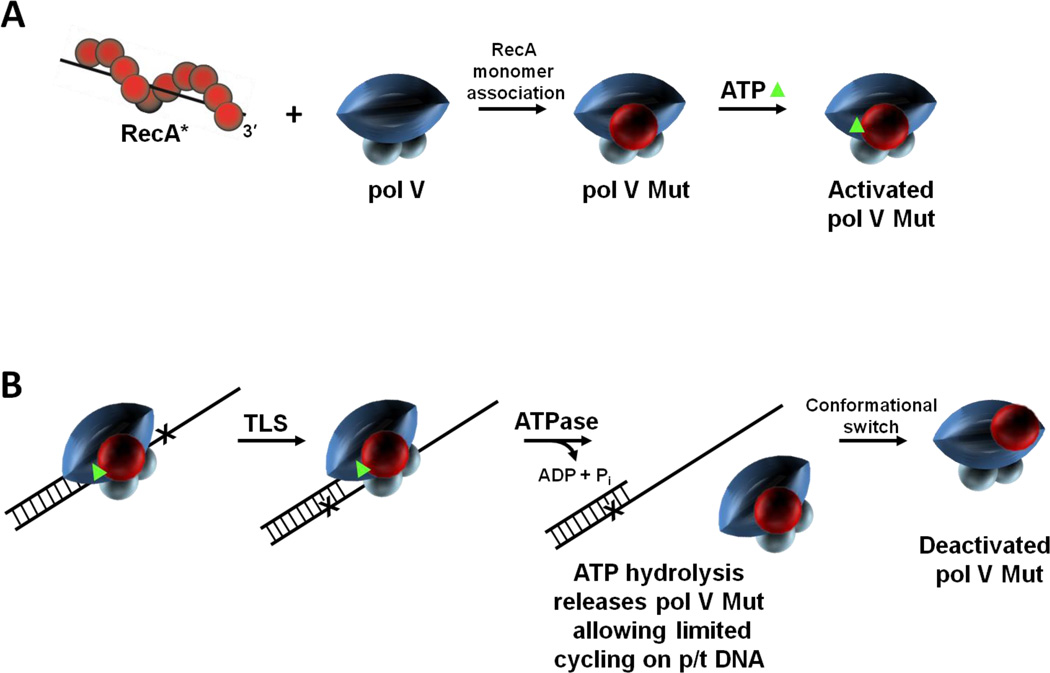
Figure 6.
RecA and ATP regulation of pol V Mut activity. Pol V activity is regulated in multiple steps. (A) First, a RecA subunit is transferred to pol V from the 3'-proximal tip of RecA* to form pol V Mut. Pol V Mut is activated by binding a molecule of ATP (green triangle). (B) Activated pol V Mut associates with p/t DNA and DNA synthesis proceeds until ATP is hydrolyzed. Pol V Mut is a unique DNA-dependent ATPase, where a single ATP hydrolytic event leads to enzyme dissociation from p/t DNA, followed by limited cycling on p/t DNA. After DNA synthesis, pol V Mut becomes deactivated but can be reactivated by exposure to a new RecA*. We propose that active and deactivated pol V Mut are determined by the location of RecA on pol V.