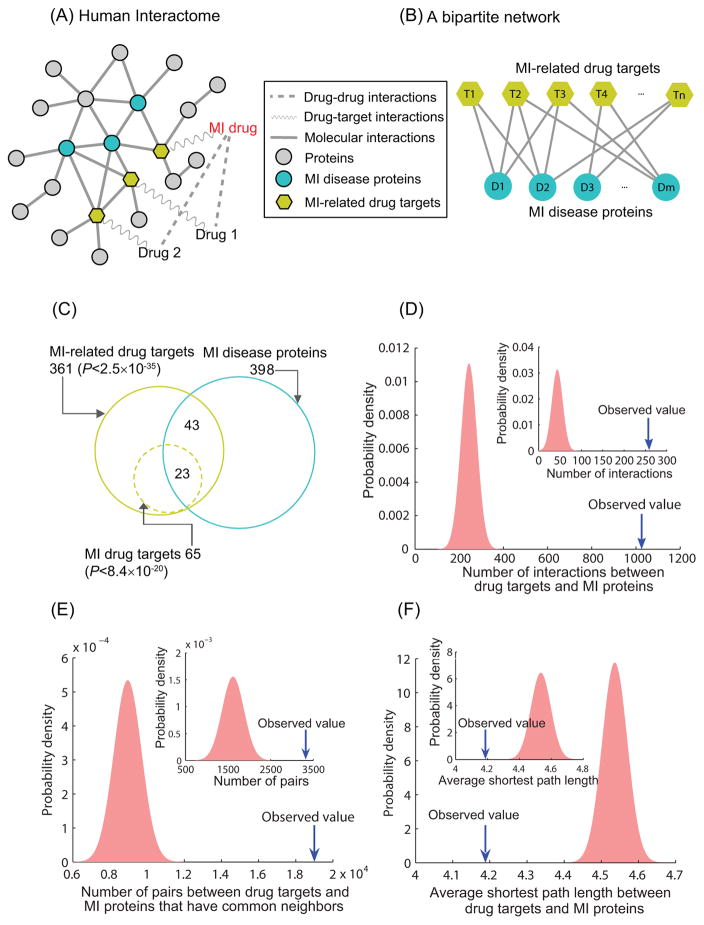
Figure 1. The closeness relationships between MI(-related) drug targets and MI disease proteins in the human interactome.
(A) MI-related drugs, drug targets, and MI disease proteins are mapped onto the human interactome. (B) A bipartite network of MI-related drug targets and MI disease proteins is constructed, and the dense associations between them are identified as drug-target-disease (DTD) modules. (C) The overlap of MI-related drug targets and MI disease proteins. (D) MI-related drug targets (MI drug target, inset) and MI disease proteins have significantly more interactions in the interactome than expected by chance. (E) There are significantly more pairs of MI-related drug targets (MI drug target, inset) and MI disease proteins with common neighbors than expected by chance. (F) The average shortest path length between MI-related drug targets (MI drug target, inset) and MI disease proteins is significantly smaller than that between two random gene sets.