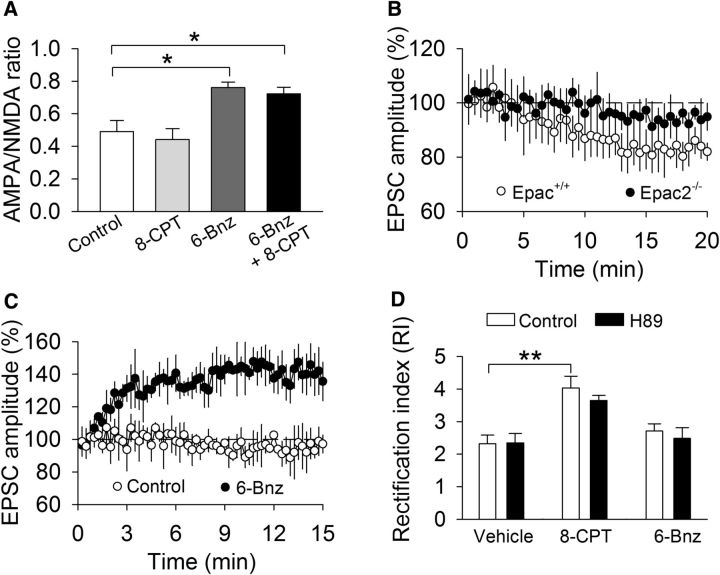
Figure 7.
Effects of activation of Epac or PKA on the AMPAR/NMDAR ratio, basal AMPAR-EPSCs, and RI in VTA dopamine neurons. A, Intracellular dialysis of 6-Bnz-cAMP (6-Bnz; 100 μm; *p = 0.013; n = 6) or 6-Bnz + 8-CPT (100 μm; *p = 0.029; n = 7) significantly increased the AMPAR/NMDAR ratio in Epac+/+ slices, whereas intracellular dialysis of 8-CPT did not significantly change the AMPAR/NMDAR ratio (p = 0.916, n = 6–7). B, Intracellular dialysis of 8-CPT caused a slow and graduate decrease in the amplitude of evoked EPSCs in Epac+/+ slices but did not significantly change EPSCs in Epac2−/− slices (p = 0.049; n = 9–10). C, Intracellular dialysis of 6-Bnz-cAMP caused rapid, robust enhancement of EPSCs in Epac+/+ slices, whereas the control internal solution did not significantly change basal EPSCs (p = 0.007, n = 10–11). D, 8-CPT increased the RI (**p = 0.003; n = 8–10). The PKA inhibitor H89 (10 μm) did not alter the RI (p = 0.941; n = 8–10), nor did it affect the 8-CPT-induced increase in the RI (p = 0.347; n = 10). 6-Bnz-cAMP did not alter the RI (p = 0.276; n = 8–9).