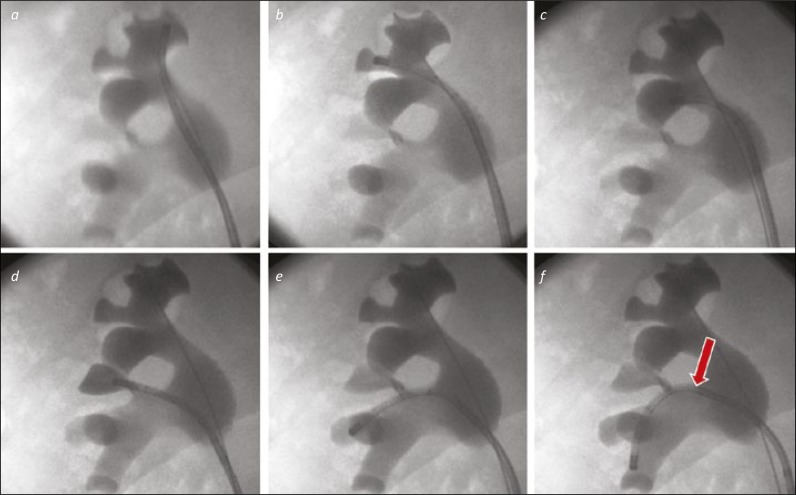
Figure 2.
A “Complete Tour” of the right kidney. 2a. The ureterorenoscope is directed to the upper medial calyx as the starting point for an anti-clockwise tour of the collecting system. 2b. The upper middle calyx will be visualised (where the safety wire is located) as the scope is moved to the upper lateral calyx. 2c. The scope is seen in the posterior upper pole calyx. 2d. The interpole, not well seen on the images 3a-c is filled with contrast via the scope to confirm it has been visualised. 2e. The scope is placed in the next calyces down, in the lateral part of the lower pole. Both calyces can be inspected in turn before moving to the lowermost calyx. 2f. The ureterorenoscope is deflected into the lower medial calyx. This required use of the secondary (passive) deflection from the renal pelvis / infundibulum to the interpole (arrow).