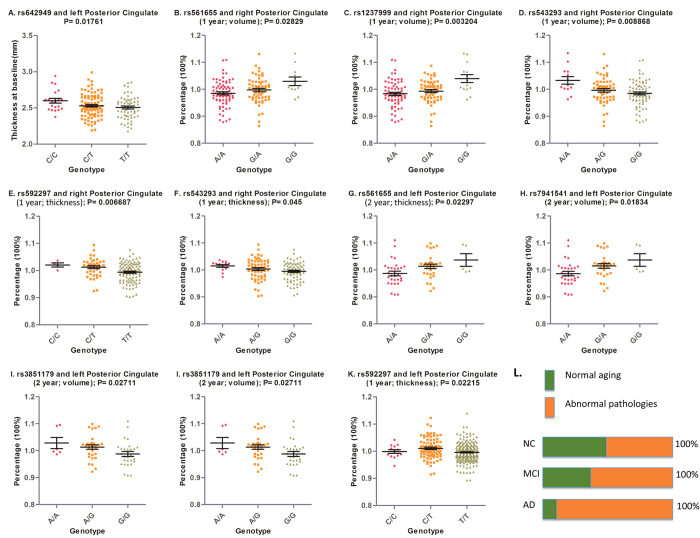
Figure 4. The significant associations of PICALM loci with baseline thickness and atrophy rate of posterior cingulate in health and MCI individuals.
(A) Depicted that rs642949 (C allele) was associated with larger thickness of posterior cingulate in NC population; (B–I) Depicted that variations of rs561655, rs1237999, rs543293, rs592297, rs7941541 were associated with slower atrophy rate of posterior cingulate in NC population; (J,K) Depicted that rs543293 and rs592297 were associated with slower atrophy rate of posterior cingulate in MCI population. (L) Depicted that the contributors to brain atrophy majorly included normal aging and pathological insults. The proportion of the latter would arise constantly as the stage progresses (from NC to MCI to AD) and finally become the predominant factor. This may explain the difference of association which PICALM genetic variations showed in NC and MCI population. Abbreviations: NC = normal cognition; MCI = mild cognition impairment; AD = Alzheimer’s disease.