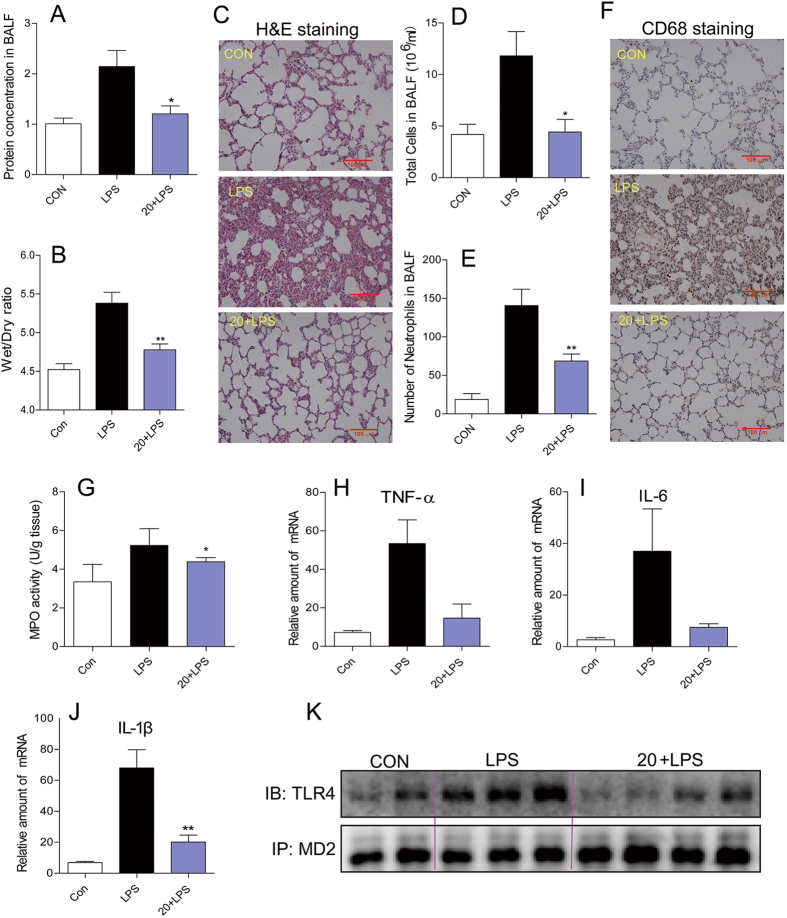
Figure 5. Effects of compound 20 on LPS-induced acute lung injury.
SD rats were treated intragastrically with compound 20 at a dosage of 20 mg/kg b.wt for one week, then challenged with 5 mg/kg LPS. Rats were euthanized with ketamine after 6 h of LPS induction. (A) Protein concentration in BALF. (B) Lung Wet/Dry ratio. (C) Histopathological changes in lung tissues determined by H&E staining. (D,E) Number of total cells and neutrophils in BALF. (F) Macrophage infiltration in lung tissue measured by CD68 immunohistochemical staining. (G) Neutrophils activity in lung tissue determined by MPO activity. (H–J) Expression of inflammatory genes in lung tissue using QPCR. (K) Immunoprecipitation assay shows that compound 20 significantly reduced the formation of TLR4-MD2 complex in lung tissue induced by LPS. Data are mean values (±SEM) of 3–5 separate experiments. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. only-LPS stimulated group. The gels were run under the same experimental conditions. Shown are cropped gels/blots (Cropped gels/blots of 5 K with indicated cropping lines are also shown in Supplementary Figure S8).