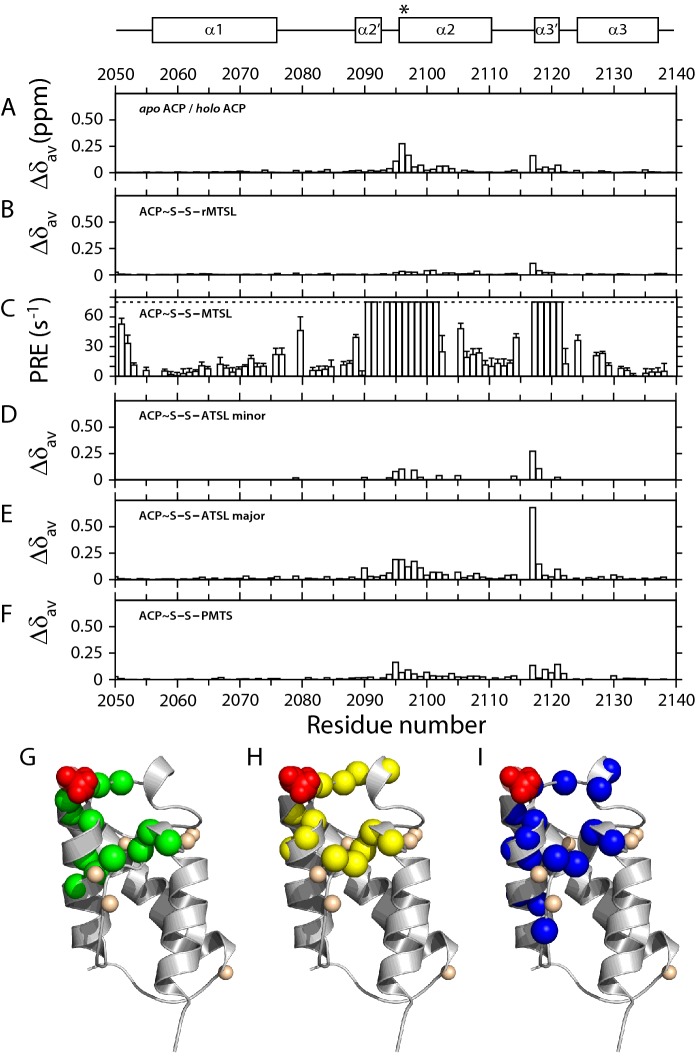
Figure 7. Average shift difference and PRE parameters for acyl-mACP9 species.
Underneath a schematic defining the boundaries of α-helices in the structure of apo mACP9, properties of disulfide-linked substrate mimics are plotted as a function of residue number. Average chemical shift differences, Δδav, are shown between holo mACP9 and (A) the apo form; (B) the reduced MTSL form; (D) the ATSL minor form (doubled peaks only); (E) the ATSL major form; and (F) the PMTS form. Panel (C) shows the PRE effects (defined as R2,MTSL – R2,ref) for MTSL-mACP9. Cartoons of the apo mACP9 structure below highlight the Ser2096 modification site in red and amide sites that: (G) show significant shift changes between the apo and holo forms (green); (H) are bleached in the MTSL form (yellow); and (I) exhibit doubled resonances in ATSL-labelled mACP9 (blue). Small cream spheres indicate the nitrogen atoms of proline residues.