Fig. 2.
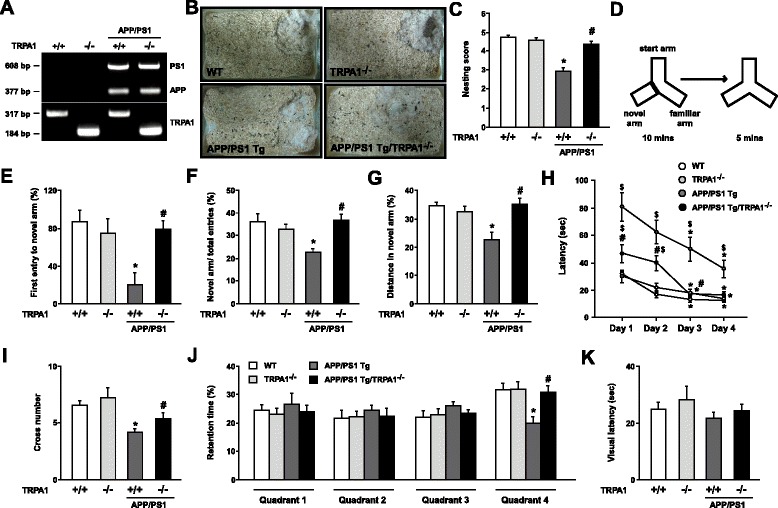
Loss of function of TRPA1 channels improves nest building and spatial learning and memory in APP/PS1 Tg mice. (a) PCR genotyping of representative WT, TRPA1−/−, APP/PS1 Tg and APP/PS1 Tg/TRPA1−/− mice. PS1 = 608 bp, APP = 377 bp, TRPA1+/+ = 317 bp and TRPA1−/− = 184 bp. (b, c) Representative examples and the score for nest building for 8-month-old WT, TRPA1−/−, APP/PS1 Tg and APP/PS1 Tg/TRPA1−/− mice. (d-g) Schematic diagram of Y-maze experimental design and ratio of first entry, number of entries and distance moved in the novel arm. (h) Morris water maze (MWM) test of learning patterns verified on days 1 to 4. (i, j) At day 5 after training, the number of times crossing the hind platform and retention times in the all quadrants. (k) The latency of arrival to the visual platform. Data are mean ± SEM from 8 mice in each group. *, P < 0.05 vs. WT mice or day 1 (h panel), #, P < 0.05 vs. APP/PS1 Tg mice, $ P < 0.05 vs. WT mice (h panel)
