Fig. 3.
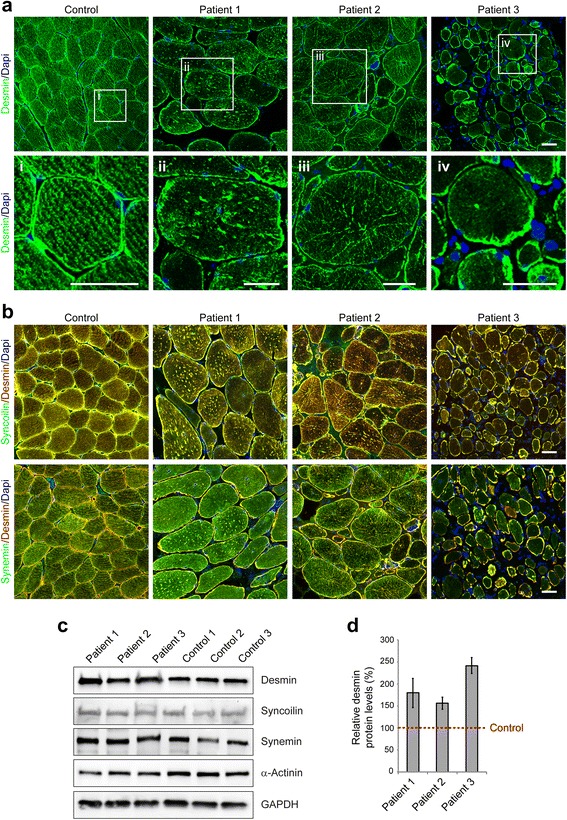
Disruption and aggregation of IF networks in EBS-MD muscle. a Confocal imaging of desmin-stained skeletal muscle specimens from a healthy control and EBS-MD patients. Panels i-iv are magnifications of the boxed areas in panel a. Note the formation of desmin-positive protein aggregates in all EBS-MD samples. Scale bars: 50 μm (a), 25 μm (panels i-iv). b Skeletal muscle sections were co-stained for desmin and synemin or syncoilin. Note that all three types of IFs lose their proper orientation in EBS-MD muscles and co-accumulate in desmin-positive protein aggregates. Scale bar: 50 μm. c Immunoblotting of cell lysates prepared from EBS-MP patients and three healthy controls. Antibodies used for detection are indicated. GAPDH and α-actinin were used as loading controls. d Signal intensities of desmin, syncoilin and synemin protein bands as shown in (c) were densitometrically measured and normalized to the total protein content (assessed by GAPDH staining). Healthy controls (dashed line) are set at 100 %. Mean values ± SEM, 3 replicates
