Fig. 2.
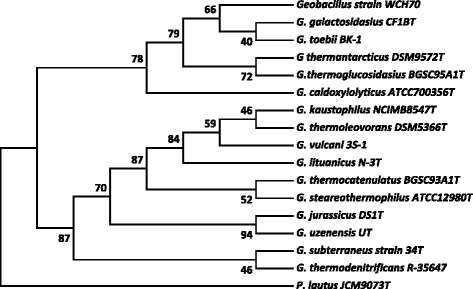
The evolutionary history was inferred by using the Maximum Likelihood method based on the Tamura-Nei model [18]. The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 500 replicates [42] is taken to represent the evolutionary history of the taxa analyzed [42]. Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in less than 50 % bootstrap replicates are collapsed. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (500 replicates) are shown next to the branches [42]. Initial tree(s) for the heuristic search were obtained automatically by applying Neighbor-Join and BioNJ algorithms to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using the Maximum Composite Likelihood (MCL) approach, and then selecting the topology with superior log likelihood value. The analysis involved 26 nucleotide sequences. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There were a total of 1271 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA5 [17]. The type strains of all validly described species are included (NCBI accession numbers): G. caldoxylosilyticus ATCC700356T (AF067651), G. galactosidasius CF1BT (AM408559), G. jurassicus DS1T (FN428697), G. kaustophilus NCIMB8547T (X60618), G. lituanicus N-3T (AY044055), G. stearothermophilus R-35646T (FN428694), G. subterraneus 34T (AF276306), G. thermantarcticus DSM9572T (FR749957), G. thermocatenulatus BGSC93A1T (AY608935), G. thermodenitrificans R-35647T (FN538993), G. thermoglucosidasius BGSC95A1T (FN428685), G. thermoleovorans DSM5366T (Z26923), G. toebii BK-1T (FN428690), G. uzenensis UT (AF276304) and G. vulcani 3S-1T (AJ293805). The 16S rRNA sequence of Paenibacillus lautusJCM9073T (AB073188) was used to root the tree
