Figure 3.
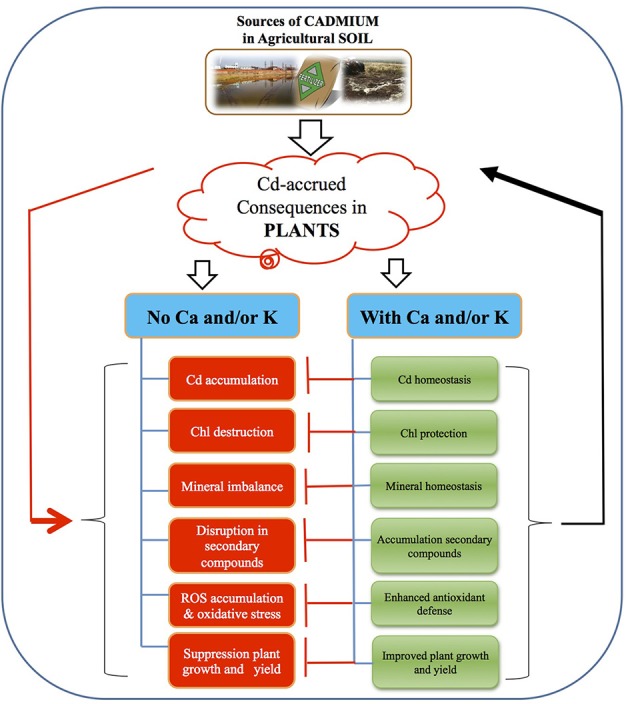
A possible model showing the strategy of calcium (Ca) and/or potassium (K) induced cadmium tolerance in chickpea. Exposure of C. arietinum to Cd caused an increased in uptake and accumulation of Cd in plant cells. Elevated cellular-Cd induced chlorophyll (Chl)-destruction, ionic disorder, disruption in secondary metabolites, generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to suppression of plant growth and yield. On the other side, supplementation of Ca and or K resulted into mineral nutrient homeostasis, increased Chl content, accumulation of secondary compounds and higher antioxidant capacity all of which contributed to the mitigation of Cd-induced damage, leading to improved plant growth and yield.
