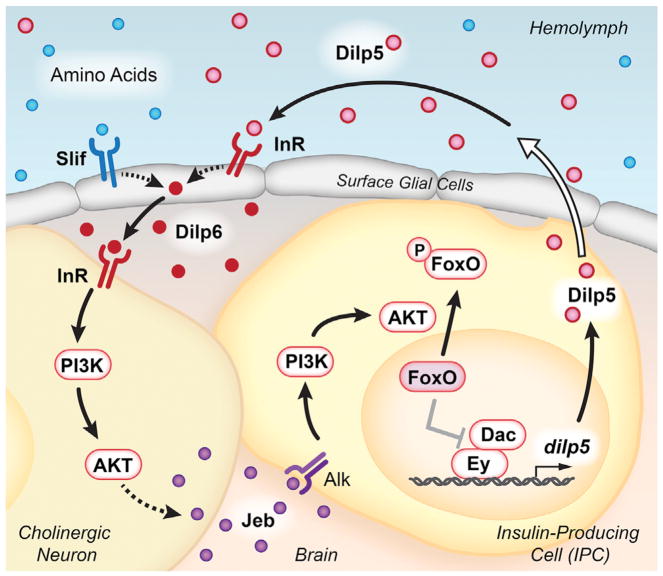
Figure 1. Intercellular Signaling Supports dilp5 Expression.
Circulating Dilps, in conjunction with dietary amino acids, promote Dilp6 production by surface glial cells. This ligand activates InR on the surface of cholinergic neurons, in close proximity to both the glia and the IPCs. IIS within cholinergic neurons leads to Jeb secretion, which activates the Alk receptor on IPCs. Downstream activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway leads to phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of Foxo. In the absence of IIS, nuclear Foxo negatively regulates the Ey and Dac transcription factors to suppress dilp5 expression. IPC-derived Dilps are secreted into the hemolymph via projections to the circulatory system (represented by the open arrow), completing the positive feedback loop.