Figure 1.
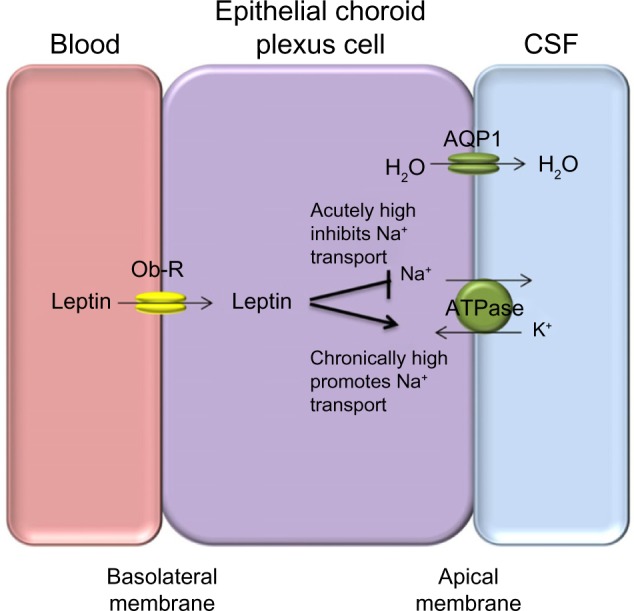
Proposed mechanism for the role of leptin in CSF secretion.
Notes: Leptin is transported into the choroid plexus via the Ob-R receptor. Acutely high levels of leptin result in decreased sodium (Na+) transport by Na+/K+ ATPase resulting in reduced movement of water (through AQP1 channels) along the osmotic gradient. Chronically high levels of leptin has an opposing effect resulting in increased Na+ movement into the CSF, consequently increasing water movement in the same direction and increasing ICP.
Abbreviations: AQP1, aquaporin 1; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; ICP, intracranial pressure.
