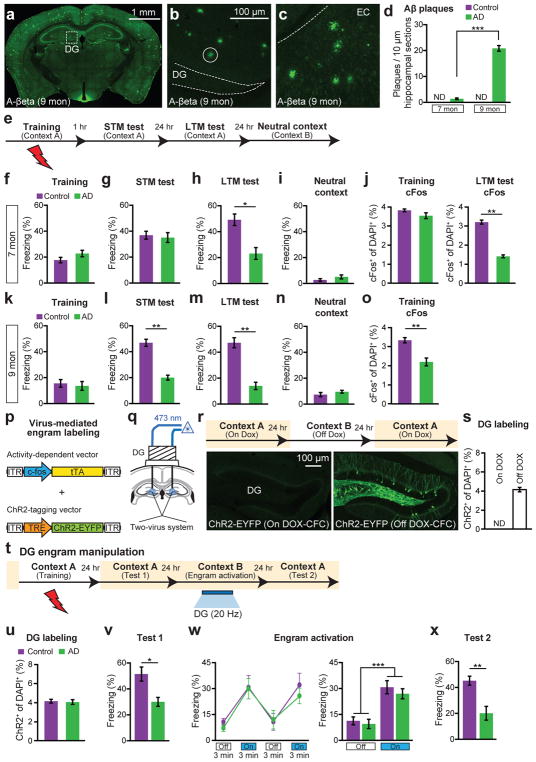
Figure 1. Optogenetic activation of memory engrams restores fear memory in early AD mice.
a–c, Aβ plaques in 9-month old AD mice (a), in DG (b), and in EC (c). d, Plaque counts in hippocampal sections (n = 4 mice per group). e, CFC behavioral schedule (n = 10 mice per group). f–i, Freezing levels of 7-month old AD groups during training (f), STM test (g), LTM test (h) or exposure to neutral context (i). j, cFos+ cell counts in the DG of 7-month old mice following CFC training or LTM test, represented in f, h (n = 4 mice per group). k–n, Freezing levels of 9-month old AD mice during training (k), STM test (l), LTM test (m) or exposure to neutral context (n). o, cFos+ cell counts in the DG of 9-month old mice (n = 3 mice per group) following CFC training represented in k. p, Virus-mediated engram labeling strategy using a cocktail of AAV9-c-fos-tTA and AAV9-TRE-ChR2-EYFP. q, AD mice were injected with the two-viruses bilaterally and implanted with an optic fiber bilaterally into the DG. r, Behavioral schedule and DG-engram cell labeling (see Methods). s, ChR2-EYFP+ cell counts from DG sections shown in r (n = 3 mice per group). ND, not detected. t, Behavioral schedule for optogenetic activation of DG engram cells. u, ChR2-EYFP+ cell counts from 7-month old mice (n = 5 mice per group). v, Memory recall in Context A 1 day after training (Test 1, n = 9 mice per group). w, Freezing by blue light stimulation (left). Average freezing for two light-off and light-on epochs (right). x, Memory recall in Context A 3 days after training (Test 2). Statistical comparisons are performed using unpaired t tests; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.