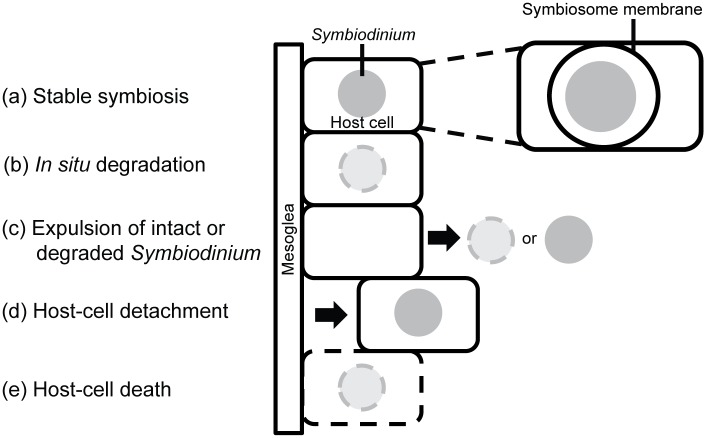
Fig 1. Four possible cellular mechanisms of cnidarian bleaching under stress.
During stable symbiosis (a), algae reside within gastrodermal cells of the cnidarian host and are surrounded by the host-derived symbiosome membrane. Under stress, algae could be lost (b) by in situ degradation (involving fusion of the symbiosome with lysosomes, autophagy, and/or a cell-death reaction of the algae themselves), (c) by expulsion of healthy and/or degraded algae, (d) by detachment of algae-containing host cells, (e) by death of algae-containing host cells through apoptosis or necrosis, or by some combination of these mechanisms.