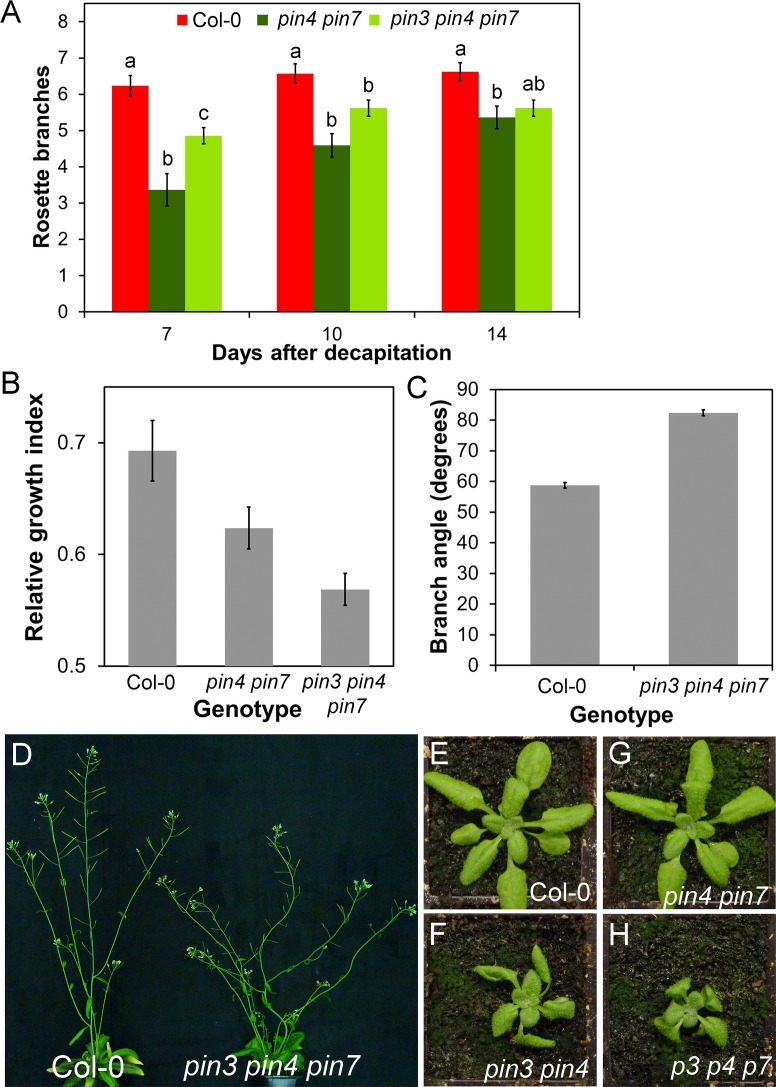
Fig 11. PIN3, PIN4, and PIN7 influence shoot branching.
A) Rosette branching in Col-0, pin4-3 pin7-1, and pin3-3 pin4-3 pin7-1 after decapitation. n = 21–22, bars indicate s.e.m. For each time point, bars with different letters are significantly different from each other (ANOVA, Tukey HSD, p < 0.05). B) Bud-bud communication in Col-0, pin4-3 pin7-1, and pin3-3 pin4-3 pin7-1. Explants were decapitated and left for 10 d. The mean relative growth index (longest branch/total branch length) was calculated for each genotype. n = 21–24; bars indicate s.e.m. Relative growth index is significantly reduced in pin4-3 pin7-1 and pin3-3 pin4-3 pin7-1 relative to Col-0 (ANOVA, p < 0.05). C) The angle formed between secondary cauline branches and the primary stem at the point of emergence in Col-0 and pin3-3 pin4-3 pin7-1. n = 45–46 cauline branches from at least 10 plants per genotype; bars indicate s.e.m. The angle is significantly different between the two genotypes (t test, n = 45–46, p < 0.005). D) Phenotype of the pin3-3 pin4-3 pin7-1 shoot system compared to Col-0 (6 wk old). E–H) Leaf phenotypes in 4-wk-old rosettes of Col-0 (E), pin3-3 pin4-3 (F), pin4-3 pin7-1 (G), and pin3-3 pin4-3 pin7-1 (H).