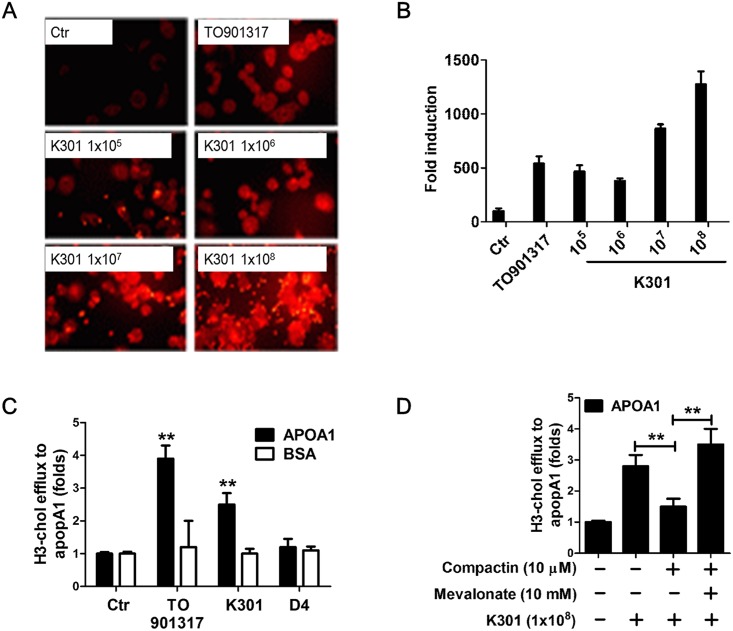
Fig 3. L. acidophilus K301 increased apoA-I mediated cholesterol efflux in macrophages.
Cholesterol efflux from [H3]-cholesterol (1 μCi/ml)-loaded macrophages to apoA-I (10 μg/ml) was measured after incubation with heat-killed L. acidophilus K301 or TO901317. (A) The binding of Alexa-labeled apoA-I onto the surface of heat-killed L. acidophilus K301 treated-macrophages is shown. (B) Densitometry analysis was performed by ImageJ software after repeated experiments. The data shown is representative of two independent experiments. (C) Cholesterol efflux is expressed as the percentage of [H3]-cholesterol in the media relative to total [H3]-cholesterol (media and cells). An unpaired t-test was used to determine the significance of differences between treatment groups and control. (D) Cholesterol efflux was examined after stimulation with heat-killed L. acidophilus K301 in the presence or absence of compactin and mevalonate. Results are the means of three independent experiments (mean±S.D). **P < 0.01 vs. untreated cells. The error bars in individual samples are shown as variations from triplicate assays.