Figure 1.
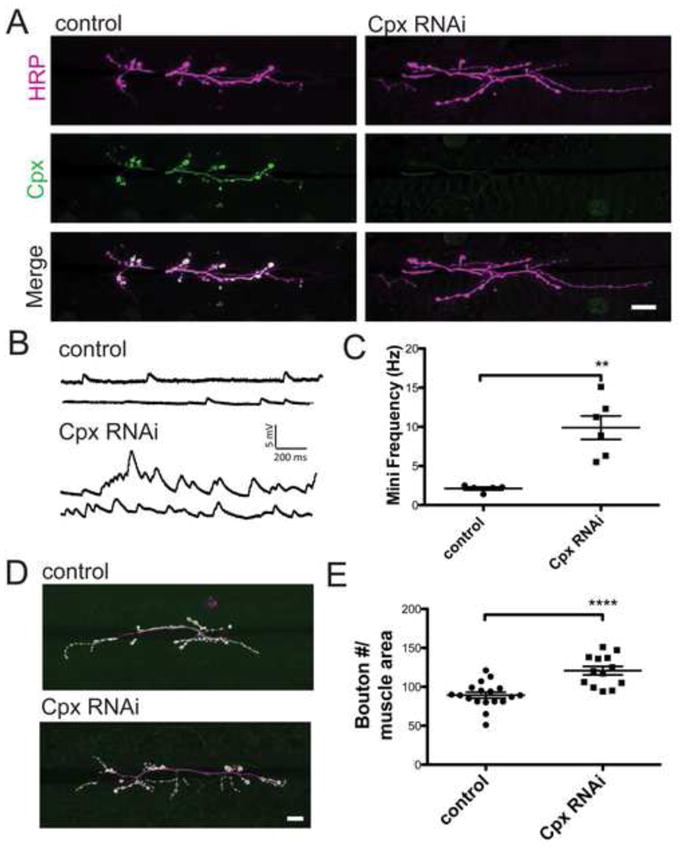
Cpx knockdown larvae exhibit increased spontaneous release and enhanced synaptic growth. (A) Expression of Cpx protein was reduced in Cpx RNAi knockdown lines (w1118; ; ) compared to control (w1118; ) using a motor neuron driver (c164-GAL4) to express Cpx-specific RNAi. Larvae were co-stained with anti-HRP and anti-Cpx specific antisera. Images were obtained from muscle 6/7 NMJs of 3rd instar larvae (B) Sample traces of spontaneous release from control and Cpx RNAi knockdown larvae. (C) Mean mini frequency (Hz ± SEM) recorded for each line. (D) Representative images of NMJs from control and Cpx RNAi knockdown larvae. Larvae were stained with anti-HRP (magenta) and anti-GluRIII (green) specific antisera to identify synaptic boutons. (E) Mean synaptic bouton number for control and Cpx RNAi knockdowns. Bouton number was normalized using muscle 6/7 area. Indicated comparisons were made using Student’s T-tests. Mean ± SEM is indicated. Scale bar = 20 μm.
