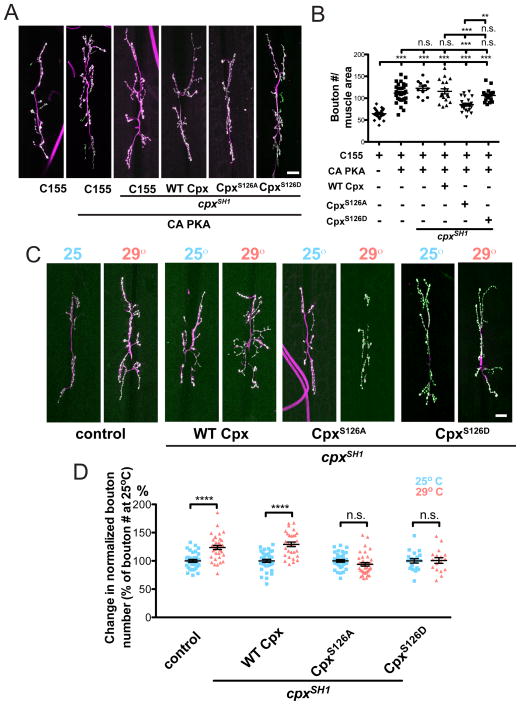
Figure 7.
Cpx PKA phosphorylation site S126 is required for PKA and activity-dependent synaptic growth. (A) Representative images of muscle 6/7 NMJs from control (C155 elav-GAL4), and lines neuronally overexpressing constitutively active PKA alone (C155; ) or in the cpxSH1 null (C155; ; cpxSH1), WT Cpx rescue (C155; ; ), CpxS126A rescue (C155; ; ), and CpxS126D rescue (C155; ; ) backgrounds. (B) Summary of mean synaptic bouton number normalized to muscle area for the indicated genetic backgrounds. Indicated comparisons were made using ANOVA with post hoc Tukey analysis. (C) Representative images of control (w1118;; CpxPE) and WT Cpx rescues (C155;; WT Cpx, cpxSH1), CpxS126A rescues (C155;; CpxS126A, cpxSH1), and CpxS126D rescues (C155;; CpxS126D, cpxSH1) reared at 25° or 29°. (D) Summary of % change in synaptic bouton number normalized to muscle area for the indicated genetic backgrounds and rearing temperatures. Synaptic bouton number was normalized to bouton number of larvae reared at 25° for each respective genotype to reflect % change. Indicated comparisons were made using Student’s T-test. Scale bars = 20 μm. Mean ± SEM is indicated in all figures.