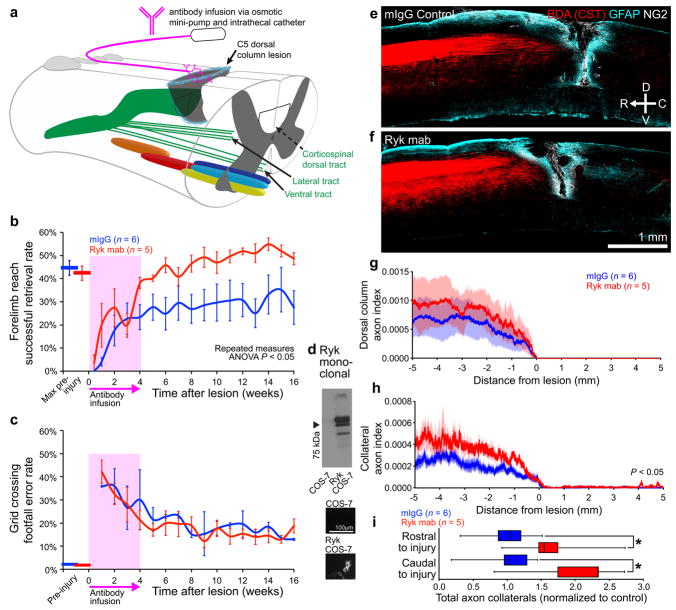
Figure 5. Monoclonal Ryk antibody infusion promotes functional recovery from spinal cord injury.
(a) Schematic showing antibody infusion by intrathecal catheterization. (b) Behavioral performance on forelimb reach skilled food-pellet retrieval task shows enhanced recovery in rats infused with Ryk monoclonal antibody for 28 days starting at time of injury (n=6 rats (IgG control), 5 rats (Ryk monoclonal), repeated measures ANOVA P=0.0354, F(1,9)=6.113). (c) Behavioral performance on skilled locomotor grid crossing task was not affected by Ryk monoclonal antibody infusion. (d) Ryk monoclonal recognizes full-length Ryk protein expressed in transfected COS-7 cells by Western and immunocytochemistry. (e–h) BDA-labeled corticospinal axons in rats infused with Ryk monoclonal antibody had greater levels of collateralization than control mouse IgG infused rats. (e,f) Images of BDA-labeled CST axons are from 6 serial sagittal cryosections spaced 280μm apart superimposed over GFAP astroglial and NG2 staining at the center of injury. (g,h) Distribution of corticospinal axons (axon index is thresholded pixels at every 0.741μm in 6 total saggital spinal cord cryosections divided by thresholded pixels in transverse pyramids) within the dorsal columns (g) or spinal gray matter (h). C5 injury site is at 0μm, rostral is represented with negative numbers, caudal with positive. (i) Sum of normalized axon collaterals over 5mm relative to control. Rats infused with Ryk monoclonal antibody had greater levels of collateralization both rostral and caudal to the lesion than control mouse IgG infused rats (n=6 rats (IgG control), 5 rats (Ryk monoclonal), one-tailed t-test *P<0.05: rostral P=0.0446 t(6)=2.000, caudal P=0.0196 t(6)=2.594). Data in (b, c, g, h) presented as mean±s.e.m., data in (i) presented as median and inter-quartile range.