Figure 8. Interaction between PlyCB and PS requires structural integrity of a cationic binding groove.
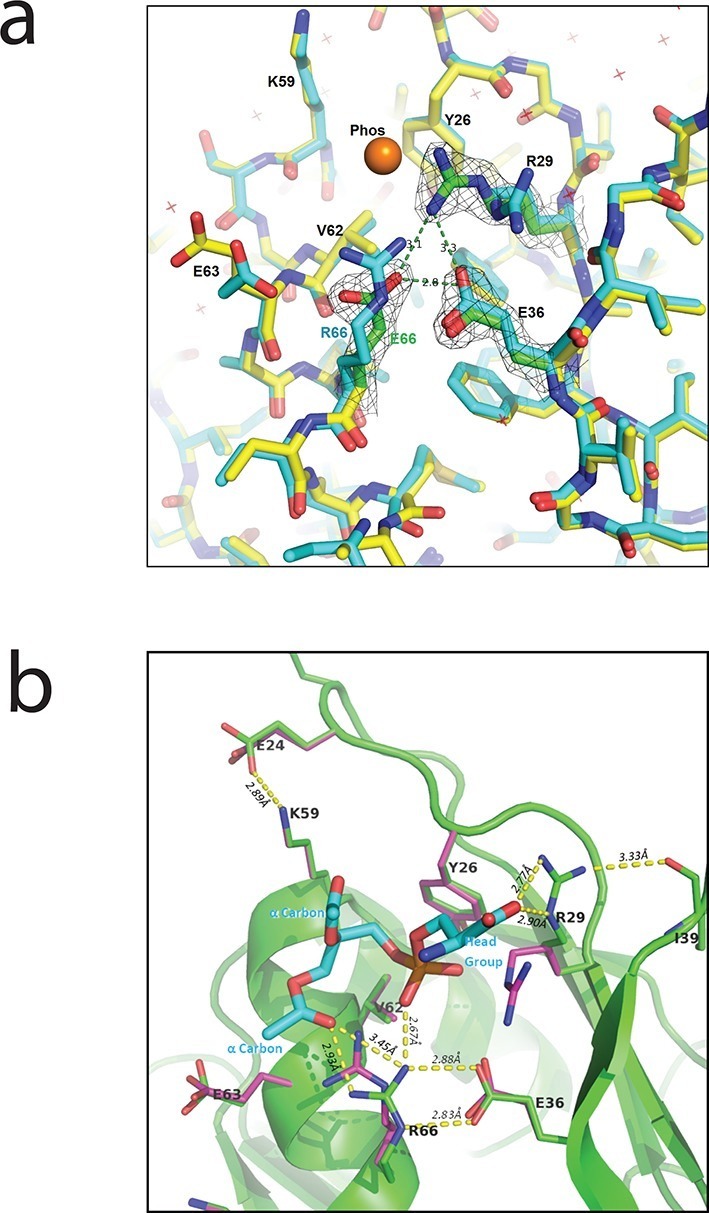
(a) Superimposed crystal structures of WT PlyCB (PDB: 4F87, cyan carbons) and PlyCBR66E (PDB: 4ZRZ, yellow, with green to emphasize the key residues R29, E36 and the mutated E66) in the groove region. These are both high-resolution structures (1.4 Å and 1.7 Å, respectively) of PlyCB alone. The orange sphere shows the location of a putative phosphate site observed in WT PlyCB in the presence of phosphate or phosphate-bearing ligands. This site holds a water molecule in the WT structure, but an empty site was observed in PlyCBR66E, apparently disrupted by the mutation. Mesh shows 2Fo-Fc electron density contoured at 1.6 σ for the three key residues in the mutant structure. The H-bond interaction between R66 and E36 is maintained in the mutant, suggesting that the observed side-chain conformations represent a stable configuration. (b) Local structure around the PS docking pose with lowest interface energy, as determined with Rosetta. The PS (cyan carbons) with partially removed fatty acid tails binds to the putative docking site adjacent to R29, K59, and R66. The headgroup and two α carbons of the fatty acid chains are labeled in cyan. The PlyCB backbone is shown in green, with the side chains in the docking site (sticks with green carbons) together with their superimposed conformations from the holoenzyme crystal structure (PDB: 4F88, magenta carbons). Interestingly, the conformation of PlyCB with a double H-bond between R66 and E36, which is the conformation seen in the PlyCB-alone high-resolution structure PDB: 4F87 (Figure 3a, 6a), is reproduced in the PS docking. Proposed H bonds and salt bridges, in the calculated PS docking, as well as the distances between the corresponding atoms are also shown (dashes and labels).
