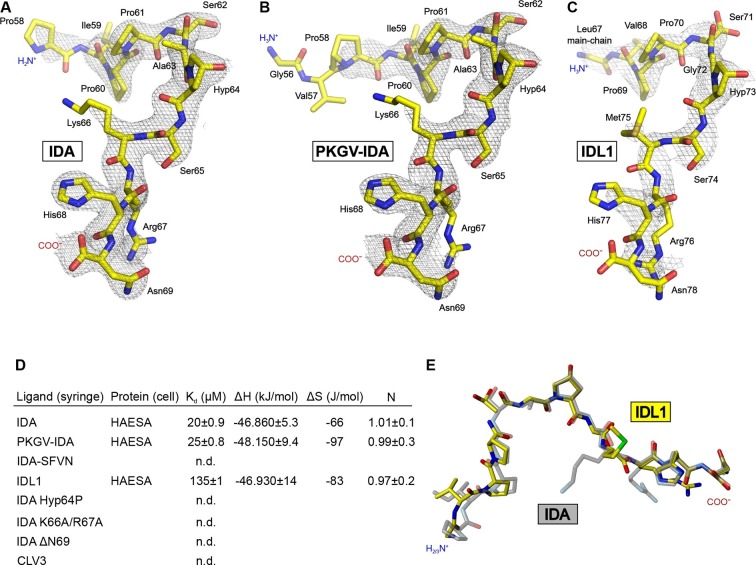
Figure 2. Active IDA-family peptide hormones are hydroxyprolinated dodecamers.
Close-up views of (A) IDA, (B) the N-terminally extended PKGV-IDA and (C) IDL1 bound to the HAESA hormone binding pocket (in bonds representation, in yellow) and including simulated annealing 2Fo–Fc omit electron density maps contoured at 1.0 σ. Note that Pro58IDA and Leu67IDA are the first residues defined by electron density when bound to the HAESA ectodomain. (D) Table summaries for equilibrium dissociation constants (Kd), binding enthalpies (ΔH), binding entropies (ΔS) and stoichoimetries (N) for different IDA peptides binding to the HAESA ectodomain ( ± fitting errors; n.d. no detectable binding). (E) Structural superposition of the active IDA (in bonds representation, in gray) and IDL1 peptide (in yellow) hormones bound to the HAESA ectodomain. Root mean square deviation (r.m.s.d.) is 1.0 Å comparing 100 corresponding atoms.