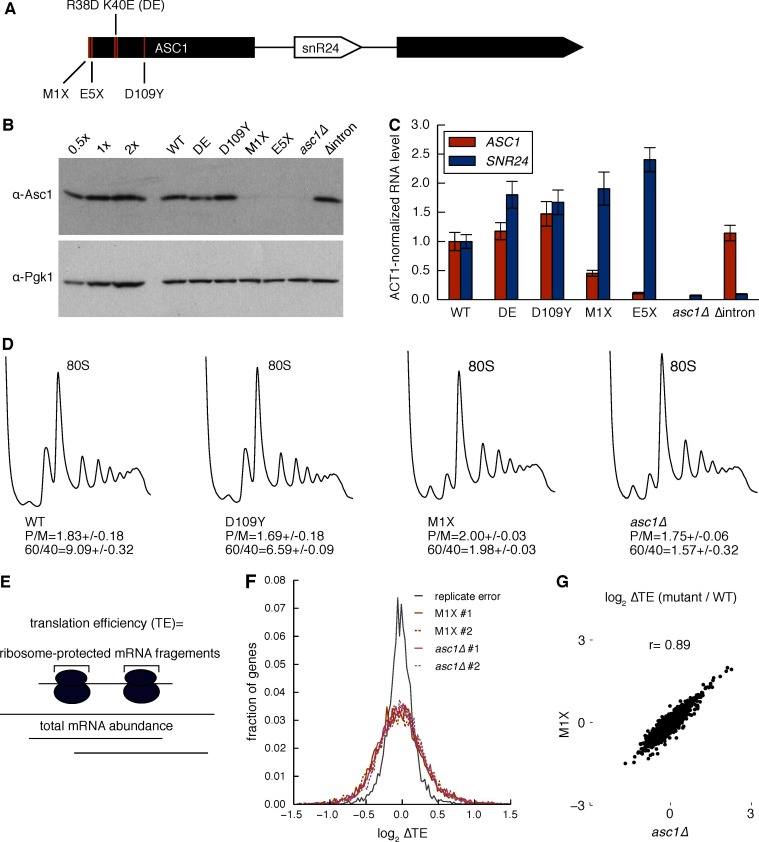
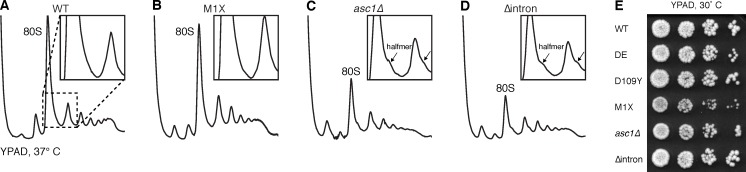
Figure 1. Loss of the Asc1 protein causes widespread changes in translation efficiency.
(A) Gene model of ASC1, showing the SNR24 snoRNA and location of protein null (M1X and E5X) and ribosome binding (DE and D109Y) mutations. (B) Asc1 protein levels quantified by Western blot. Pgk1 blot on the same membrane is shown as a loading control. Dilutions of the WT sample are shown on the left. Data is representative of three biological replicates. (C) ASC1 mRNA and SNR24 snoRNA levels quantified by qRT-PCR. Levels were normalized to ACT1 mRNA levels. Error bars represent s.d. from three technical replicates. Data is representative of three biological replicates. (D) Polysome profiles of the ASC1 mutants at 30˚C. The polysome/monosome (P/M) ratio and 60S/40S (60/40) ratio are shown with s.d. from two biological replicates. (E) Calculation of translation efficiency as the ratio of ribosome-protected mRNA fragments to total mRNA abundance. (F) Distribution of changes in TE comparing two biological replicates from WT cells (i.e. replicate error) or asc1-M1X or asc1∆ to its corresponding WT comparison. #1 and #2 denote biological replicate experiments. (G) Scatterplot of TE changes between the two ASC1 null mutants. The Pearson correlation coefficient is shown.