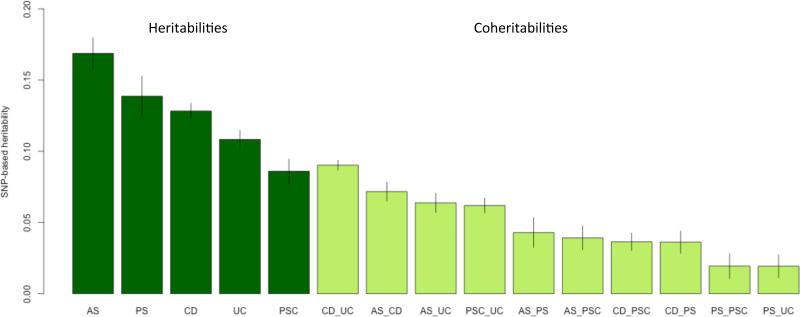
Figure 4. Estimation of Immunochip-wide pleiotropy (excluding the MHC region) between the five diseases under study.
Proportion of genetic variance in liability (SNP-based heritability) and proportion of genetic covariance in liability between diseases (SNP-based coheritability) with 95% error bars (see Supplementary Table 15a; estimates including MHC SNPs see Supplementary Table 15b). Disease-associated SNP markers from Supplementary Table 3a (at a maximum of 244 independent signals from 169 non-MHC risk loci, see also Supplementary Figure 6) explain 42.2% of AS-, 79.63% of CD-, 39.6% of PS-, 29% of PSC- and 55% of UC-Immunochip-wide SNP-heritability (excluding the MHC region) on the liability scale, respectively. As the Immunochip densely tags common variants but at the cost of losing genome-wide coverage, the estimated SNP-heritabilities are lower bounds for genome-wide SNP-heritabilities.