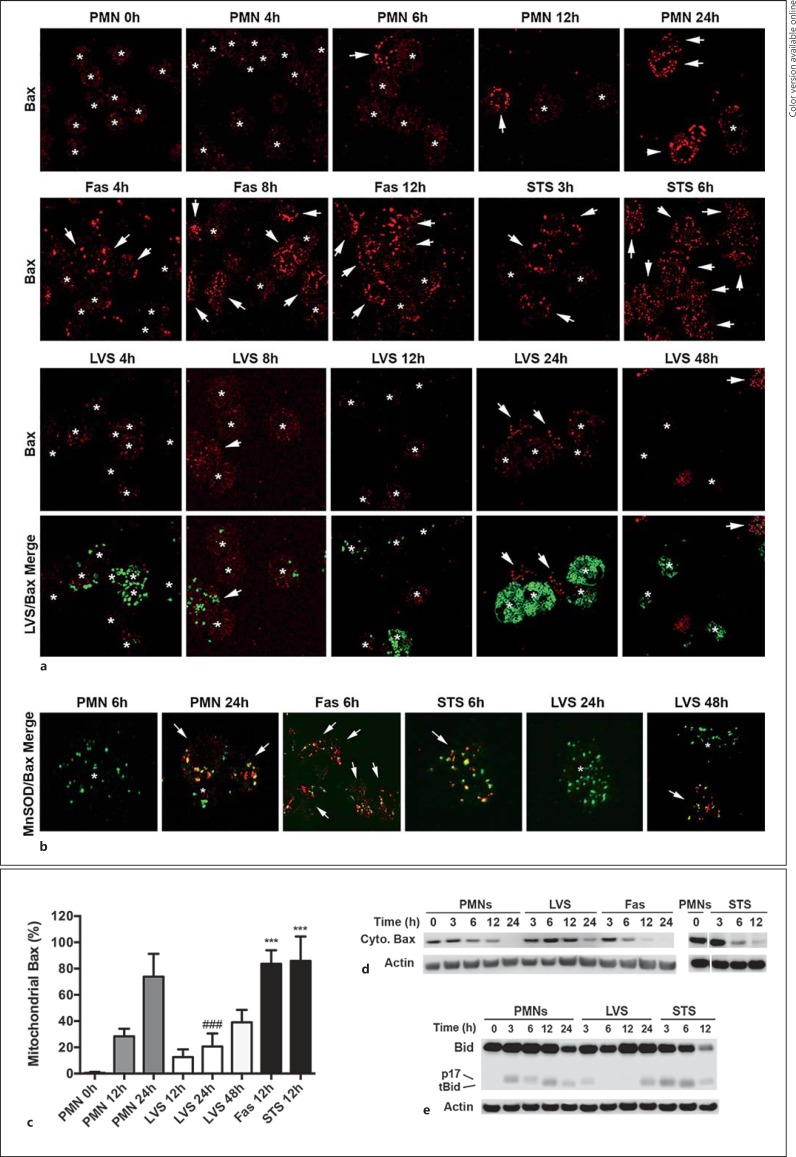
Fig. 3.
F. tularensis inhibits Bax translocation to mitochondria. Neutrophils were left untreated, infected with LVS or were treated with Fas-crosslinking antibodies or STS as indicated. a Bax translocation to and accumulation on neutrophil mitochondria were assessed at the indicated time points by confocal microscopy. Representative images show Bax (red) and LVS (green). Arrows and asterisks indicate PMNs that do and do not show mitochondrial Bax accumulation, respectively. b Merged confocal images show the extent of Bax (red) colocalization with the mitochondrial marker MnSOD (green). Arrows and asterisks indicate PMNs that do and do not show mitochondrial Bax accumulation, respectively. Colors refer to the online version only. c Pooled microscopy data indicate the kinetics of Bax translocation. Data are the mean ± SD from 8 independent experiments. *** p < 0.001 vs. control and LVS-infected PMNs at 12 h. ### p < 0.001 vs. control PMNs at 24 h. d Immunoblots indicate the kinetics of Bax disappearance from PMN cytosol. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. e Immunoblots show the extent of Bid (22 kDa) processing to its proapoptotic truncated (tBid) 15-kDa form or a p17-kDa form of unknown function. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. β-actin was used as the loading control.