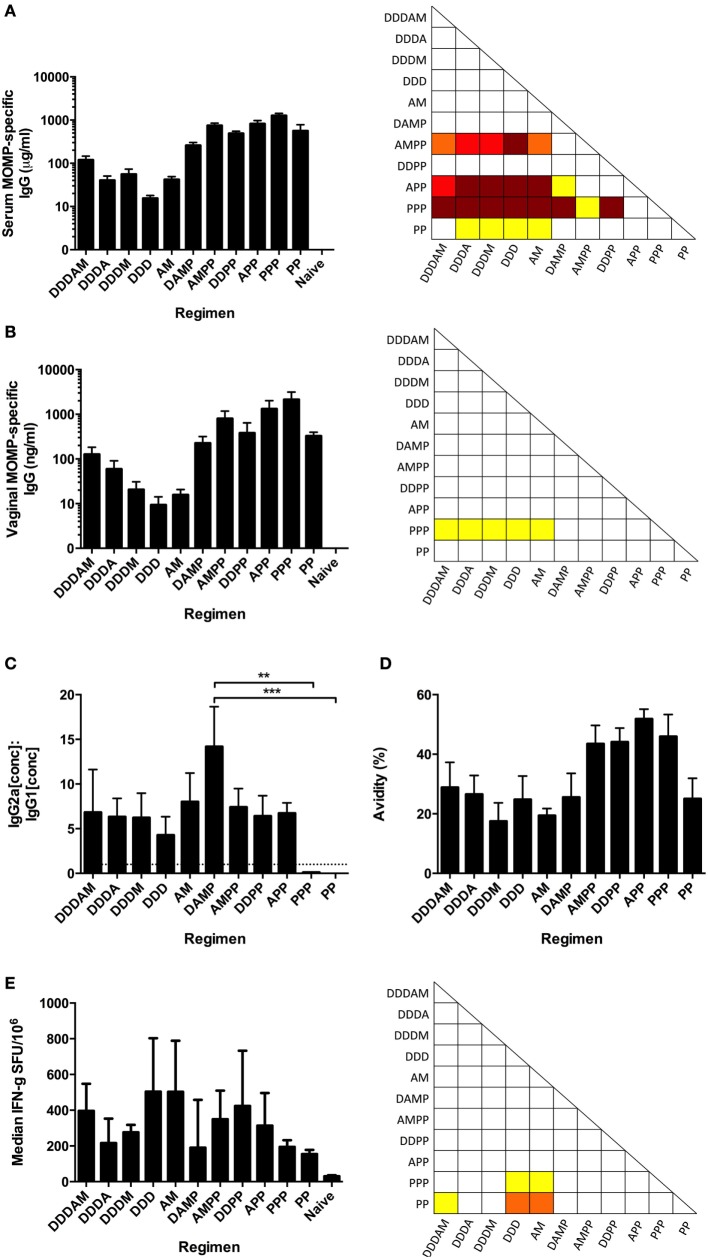
Figure 2.
Antibody and cellular responses following multi-component prime-boost vaccination regimens. BALB/c mice (n = 8 per group) were intramuscularly immunized in various prime-boost regimens, with sera and vaginal wash collected 2 weeks after final boost. MOMP-specific IgG concentrations were measured in serum (A) and vaginal washes (B), expressed as the mean + SEM concentrations. (C) Serum MOMP-specific IgG2a and IgG1 isotype concentrations were measured by ELISA, and the mean + SEM IgG2a:IgG1 ratios plotted. The dotted line indicates the IgG2a:IgG1 ratio of 1, demonstrating Th1-skewing above this line or Th2-skewing below it. (D) Serum antibody avidity was measured by MOMP-specific IgG ELISA with non-reducing (H2O) and reducing (8 M urea) washes after sample addition. Results are shown as percentage (%) change in binding (reducing OD450/non-reducing OD450 × 100). IgG concentrations, avidities, and IgG2a:IgG1 ratio represented as group means and SEM. (E) Vaccinated BALB/c mice (n = 8 per group) were sacrificed 1 week post-final immunization and splenocytes assessed by IFN-γ ELISpot for MOMP-reactive T cells stimulated by a peptide pool consisting of 15-mers overlapping by 11 amino acids. Data expressed as group medians (+ interquartile range) (SFU/million antigen stimulated cells). *p ≤ 0.05 (yellow), **p ≤ 0.005 (orange), ***p ≤ 0.0005 (red), and ****p ≤ 0.0001 (dark red) by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison post-test on logged values (A–D) and by Kruskal–Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparison test (E).