Figure 4.
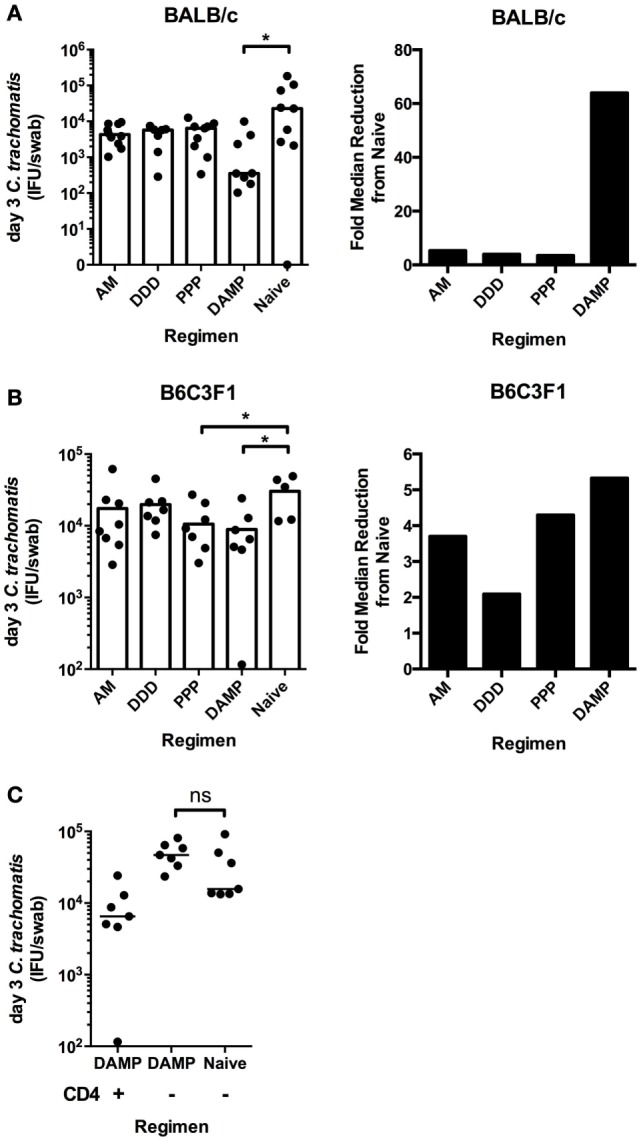
The DAMP vaccine regimen enhances the clearance of intravaginal C. trachomatis in BALB/c and B6C3F1 mice, in a CD4+ T-cell-dependent manner. Six weeks after the final vaccination and 1 week after 2 mg/mouse subcutaneous Depo-Provera treatment, BALB/c and B6C3F1 mice (n = 7–10 per group) were infected intravaginally with 4 × 105 IFU of C. trachomatis D/UW-3/Cx. The vaginal vault of mice were sampled using individual swabs at day 3 [(A) BALB/c; (B) B6C3F1] after challenge, and vaginal Chlamydial loads quantified by infection assay and immunoflorescent microscopy. The fold reduction in median Chlamydial load compared to naive BALB/c (A) and B6C3F1 (B) mice at day 3 after infection is also represented. (C) B6C3F1 mice (n = 8 per group) were immunized with the DAMP regimen or left unvaccinated and subsequently depleted of CD4+ T cells by i.p. injections of 500 μg/mouse of anti-mouse CD4 monoclonal antibody (clone GK1.5) on days −1 and +1 with respect to day of challenge day 0. C. trachomatis load was measured in the vaginal vault at day 3 after infection. Individual and median values are represented. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, and ***p ≤ 0.001, two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test.
