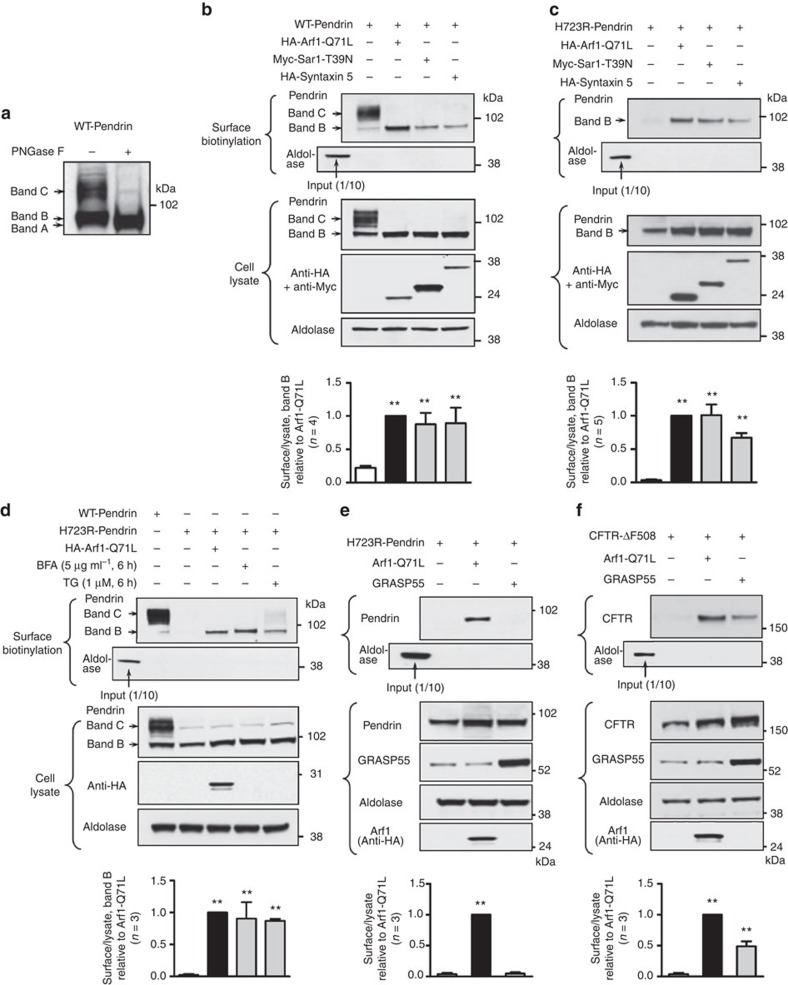
Figure 1. Cell-surface expression of H723R-pendrin by unconventional protein secretion.
(a) PANC-1 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding wild-type (WT)-pendrin. Protein samples were treated with N-glycosidase F (PNGase F), which deglycosylates all N-glycan chains and immunoblotted with anti-pendrin antibodies. Band A: deglycosylated pendrin, band B: immature core-glycosylated pendrin, band C: mature complex-glycosylated pendrin. (b,c) Surface biotinylation assays were performed in PANC-1 cells expressing WT- (b) or H723R- (c) pendrin. In control cells (first lanes in b and c), the band C form of WT-pendrin and no form of H723-pendrin were expressed on the cell surface. Blockade of ER-to-Golgi traffic by overexpression of Arf1-Q71L, Sar1-T39N or syntaxin 5 induced the cell-surface expression of core-glycosylated (band B) WT- and H723R-pendrins. The absence of the cytosolic protein aldolase A in the biotinylated fraction confirmed cell surface protein-specific labelling in each experiment (input: 40 μg of cell lysate, surface biotinylation: 400 μg protein). (d) Treatments with brefeldin A (BFA) or thapsigargin (TG) also induced cell-surface expression of H723R-pendrin in PANC-1 cells. (e,f) Whereas GRASP55 overexpression induced cell-surface expression of ΔF508-CFTR in PANC-1 cells (f), GRASP55 was not effective in inducing cell-surface expression of H723R-pendrin (e). Quantitation of multiple experiments is presented under each immunoblot. **P<0.01 by one-way analysis of variance, compared with lane 1, the number of replicates (n) is presented in each panel. Unprocessed original scans of western blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 10.