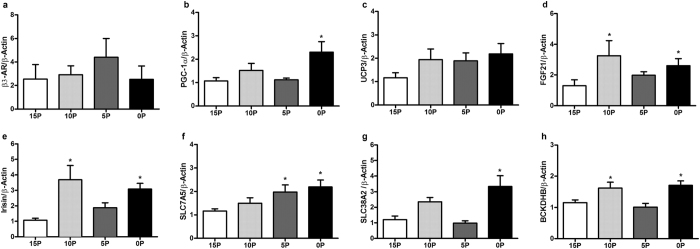
Figure 7. Effects of low protein diets on relative mRNA abundance of key regulatory molecules of energy metabolism in skeletal muscle.
(a) β3-AR (β3-adrenergic receptors), (b) peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 α (PGC1-α), (c) uncoupling protein 3 (UCP3), (d) fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), (e) irisin, (f) solute carrier family 7 member 5 (SLC7A5), (g) solute carrier family 38 member 2 (SLC38A2) and (h) branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase E1, beta polypeptide (BCKDHB) in obesity-prone rats. The animals were fed either a control (15% protein; 15P), moderately low protein (10% protein; 10P), very low protein (5% protein; 5P) or protein-free (0% protein; 0P) isocaloric diet for 14 days. The relative mRNA abundance was determined by qPCR using β-Actin as reference target. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 5–9. *P < 0.05 vs 15P.