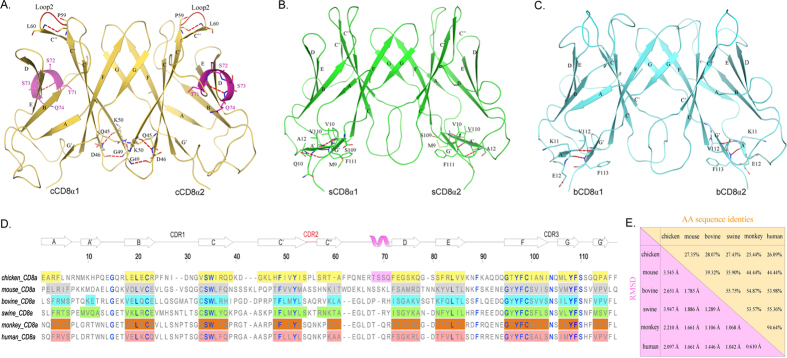
Figure 1. Structural characteristics and comparison of cCD8αα, sCD8αα and bCD8αα homodimers.
The overall structures of cCD8αα, sCD8αα and bCD8αα and their distinct characteristics are shown in (A–C). The β-strands and specific residues are labelled. Hydrogen bonds are shown as red dashed lines. (A) The cCD8αα homodimer is coloured yellow-orange, and its unique helix is coloured light magenta; its extremely short CDR2-like loop, which only consists of 2 residues, is coloured red. (B) The sCD8αα homodimer is coloured green, and the composed residues of its additional A’ strand are displayed. (C) The bCD8αα homodimer is coloured cyan, and its A’ strand was also determined. (D) The AA alignment of CD8α molecules based on their crystal structures is shown. Each strand consisting of residues is labelled by a coloured box: yellow-orange for chicken, grey for mouse (PDB ID: 3DMM), green for swine, cyan for bovine, orange for monkey (PDB ID: 2Q3A) and salmon for human (PDB ID: 1CD8). The hollow arrow on the regions of boxes represents the corresponding strand, and the only helix in cCD8αα is also labelled by a light magenta box. The highly conserved residues are coloured blue. (E) The values of AA identities and RMSDs of the CD8α molecules whose structures have been resolved are shown.