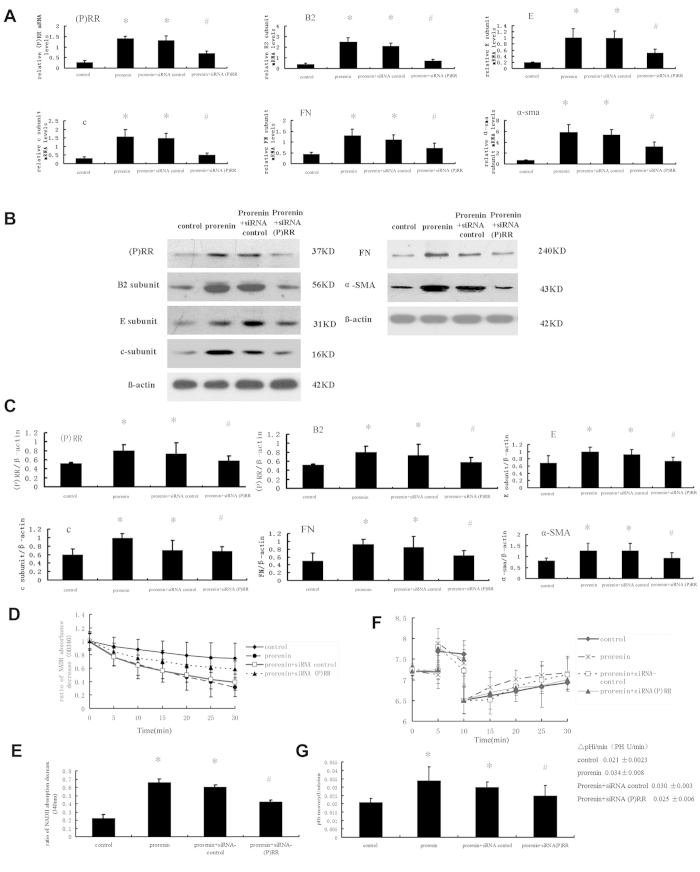
Figure 7. Effects of small interfering (si) RNA-mediated silencing of (P) RR on expression of fibrosis marker (FN and α-SMA), V-ATPase subunits (B2, E, and c) and activity in NRK52E cells after stimulation by prorenin (100 pmol/L) for 48 h.
Cells were divided into the four groups as follows: control group, prorenin-treated group, prorenin-treated groups transfected with non-silencing siRNA (siRNA-control) or specific (P) RR siRNAs (siRNA- (P) RR). (A) mRNA levels of (P) RR, V-ATPase subunits (B2, E, and c), and fibrosis marker (FN and α-SMA) in NRK52E cells by groups. Values are with means ± SD; n = 6; *P < 0.05 vs. control group, #P < 0.05 vs. prorenin-treated group. (B) Western blots analysis of (P) RR, V-ATPase subunits (B2, E, and c), and fibrosis marker (FN and α-SMA) in NRK52E cells by groups. (C) Graphic representation of the protein levels. Values are with means ± SD; n = 6; *P < 0.05 vs. control group, #P < 0.05 vs. prorenin-treated group. (D) Line graph showed as the results of ATP/NADH-coupled assay in different stimulated groups. (E) Bar graph showed the ratio of NADH absorption decrease at OD340 (ATP hydrolysis). Compared to the prorenin-treated group, the ATPase activity in the siRNA-(P) RR group was lower (0.420 ± 0.019 vs. 0.664 ± 0.04 OD units/min), n = 6; #P < 0.05 vs. prorenin-treated group *P < 0.05 vs. control group. (F) The Na+-independent intracellular pH (pHi) recovery after acute cellular acidification methods was measured as the proton-translocating activity of V-ATPase by groups. The effect of a Na+-free solution (CHB) on the pH recovery of NRK52E cells, which was mainly mediated by V-ATPase, was depicted in the control groups (♦), prorenin-stimulated groups (*), and prorenin-treated group transfected with non-silencing siRNA (siRNA-control) (□) or specific (P) RR siRNAs (▲). (G) The rate of pHi recovery of different groups. Values are with means ± SD; n = 6. *P < 0.05 vs. control group, #P < 0.05 vs. prorenin-treated group.