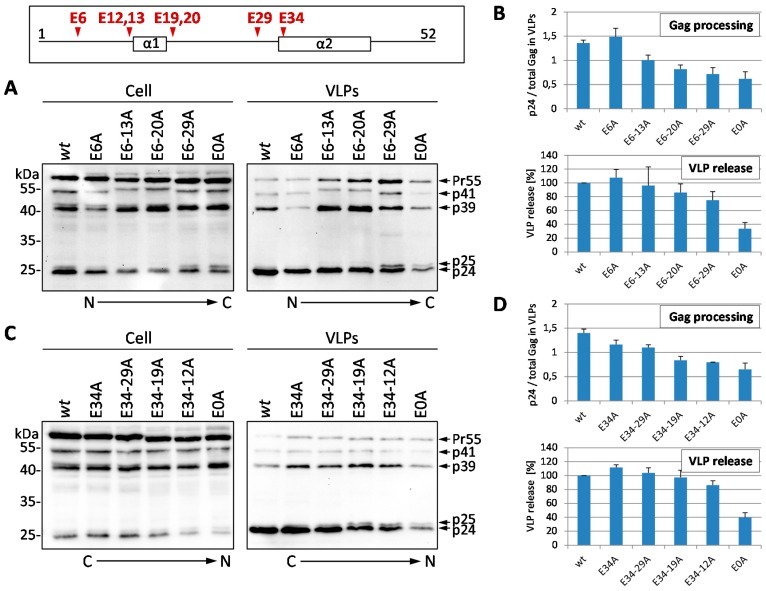
Figure 2.
Successive mutation of glutamic acids in p6 leads to a dose-dependent defect in Gag processing and impaired VLP release. (A,C) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the HIV-1 expression plasmid pNLenv1, coding either for the wt or mutants carrying Glu to Ala mutations, either from the N- (A) or from the C-terminus (C) of p6. Whole cell lysates and VLP fractions were analyzed by western blotting using anti-CA antibodies (B,D). The VLP release was calculated as the amount of CA in the VLP fraction relative to the total amount of Gag detected in cell and VLP fractions. Values on the y-axis were adjusted to 100% for wt. Rate of Gag processing was calculated as the amount of CA relative to the total amount of Gag in each VLP fraction. Resulting ratios were normalized by mean of all values of each experiment (adapted from [53]). Values on the y-axis represent arbitrary units. Bars represent the mean values of 3 independent experiments ± SD.