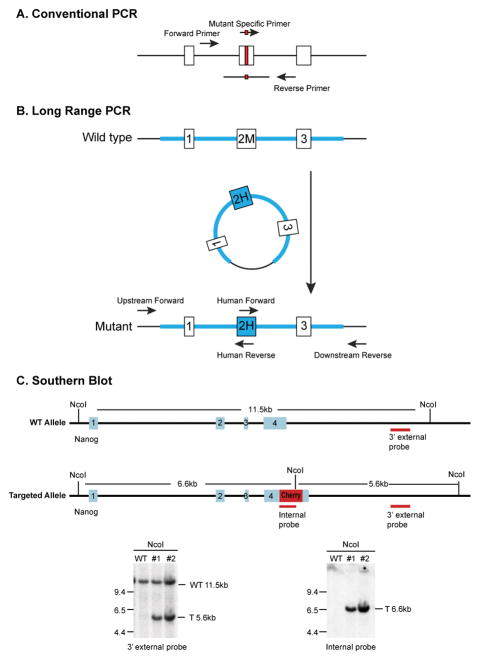
Figure 5.
Genotyping Strategies. (A) Genotyping by conventional PCR. For Indel models, a pair of PCR primers encompassing the target region is used. For HDR models mediated by a donor oligonucleotide, the pair of primers should be positioned 5′ and 3′ to the region overlapping with the donor oligonucleotide. In addition, mutant specific primers can be designed to amplify only the mutant allele. (B) Genotyping by long range PCR. If a model is created mediated by a donor plasmid, the mice can be genotyped by a pair of primers with the upstream or downstream primer positioned outside of the homology arm and the second primer unique to the transgene sequence. (C) Genotyping by Southern blot. Southern blot can be used to assess successful integration of the transgene into the target genomic locus. In this example, Nco1 digestion releases an 11.5 Kb genomic DNA fragment from the Nanog locus from the wild type mice. When the mCherry transgene has been successfully inserted into the Nanog locus, it brings along an additional Nco1 site, generating a 5.6 Kb genome fragment in mutant mice that could be detected by the 3′ probe located outside of the 3′ homology arm. Southern blot with a probe from the mCherry gene confirms there is only one integration event per genome.