Figure 7.
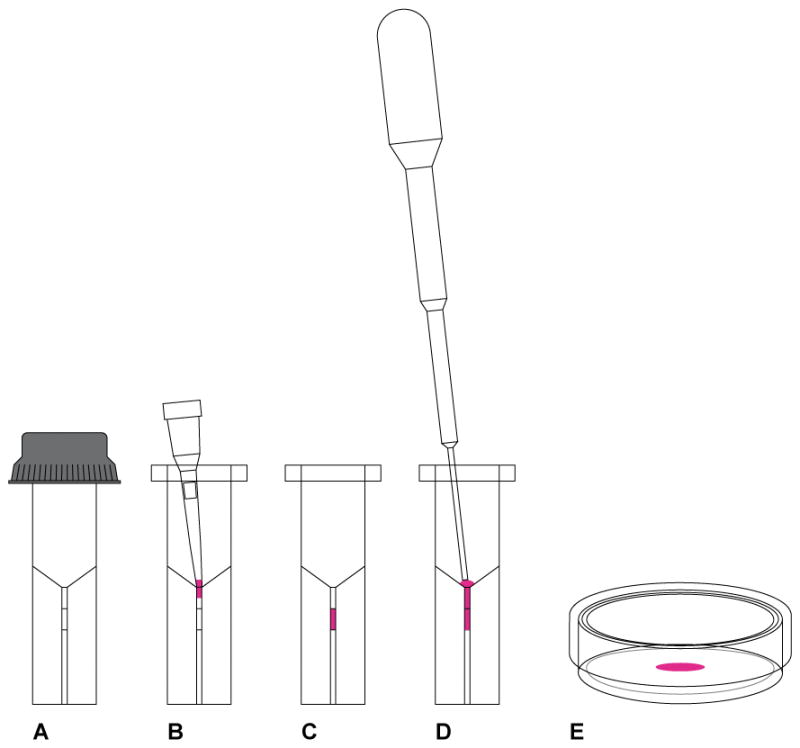
CRISPR-Cas9 delivery by electroporation. (A) We use the ECM 830 Square Wave Electroporation System from Harvard Apparatus and the electroporation cuvette from the same vendor (Cat. No. 45-0124) with 1 mm gap between the electrodes. The minimum volume is 20 μL and maximum 90 μL. (B) The 20 μL of embryos suspended in the CRISPR-Cas9 reagents is loaded into a 20 μL pipette tip and ready to be released into the chamber of the cuvette. (C) The 20 μL of embryos suspended in the CRISPR-Cas9 reagents is released into the chamber and spread evenly at the bottom of the chamber by gentle tapping. The cuvette is then transferred to the electroporator and pulses delivered. (D) Use the sterile plastic transfer pipette that comes with the cuvette to pick up 100 μL of prewarmed and pre equilibrated KSOMaa Evolve/BSA (1 mg/mL) media and release the content into the bottom of the cuvette. (E) Pipet a few times to release the embryos that may have adhered to the wall of the chamber and transfer to a 35 mm Petri dish and get the embryos ready for transfer into pseudopregnant female mice.
